Nondifferentiable Optimization: Difference between revisions
SYSEN5800TAs (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Author: Kevin Afoakwah (ka475), Meghna Sen (ms3398) | Author: Kevin Afoakwah (ka475), Meghna Sen (ms3398) (ChemE 6800 Fall 2024) | ||
Stewards: Nathan Preuss, Wei-Han Chen, Tianqi Xiao, Guoqing Hu | Stewards: Nathan Preuss, Wei-Han Chen, Tianqi Xiao, Guoqing Hu | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
=Solution Methods= | =Solution Methods= | ||
Solution of differentiable problems and differentiable cost functions can in general forms be solved with gradient based analytical methods such as the Kuhn-Tucker model and through numerical methods such as steepest descent and conjugate gradient. However the introduction of non-differentiable points in the function invalidates these methods, steepest descent cannot be calculated for a vertical line. A common method for solution of a non-differentiable cost function is through transformation into a non-linear programming model where all of the of new functions involved are differentiable such that solution is now possible through ordinary means. < | Solution of differentiable problems and differentiable cost functions can in general forms be solved with gradient based analytical methods such as the Kuhn-Tucker model and through numerical methods such as steepest descent and conjugate gradient. However the introduction of non-differentiable points in the function invalidates these methods, steepest descent cannot be calculated for a vertical line. A common method for solution of a non-differentiable cost function is through transformation into a non-linear programming model where all of the of new functions involved are differentiable such that solution is now possible through ordinary means. | ||
==Subgradient Method== | |||
The subgradient method is an optimization technique used for minimizing non-smooth convex functions. It is particularly useful when the objective function is non-differentiable. Subgradients are almost identical to simple gradients since the convex functions are differentiable at any point, however, the key difference is in the step size when referring to the method of steepest descent. Non-differential function’s most optimal point might be a non-differential point and will not converge to zero like a simple gradient. Therefore, subgradients relax these step-size rules to find the appropriate optimal point by generalizing gradient descent and using minimization techniques. | |||
'''Algorithm Steps:''' | |||
Assumptions: The function is convex | |||
# Initialization: Start with initial point x<sub>0</sub> and step size t<sub>0</sub> | |||
# Iterative Update: At each iteration k: | |||
## Compute the subgradient g<sub>k</sub> of the function f(x) at the current point x<sub>k</sub> | |||
## Update the current point using formula<math>[x_{k+1} = x_k + t_kg_k]</math> | |||
## Update the step size t<sub>k</sub> according to a predefined rule | |||
# Convergence Check: Repeat iteration updates until a stopping criterion is met. This can be when there is a maximum number of iterations, or a sufficiently small change in function value. | |||
==Simple Kink Case== | ==Simple Kink Case== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 72: | ||
Return to step 2 to iterate until convergence. | Return to step 2 to iterate until convergence. | ||
This method is not only guaranteed to converge but progress towards convergence is made with each iteration. | This method is not only guaranteed to converge but progress towards convergence is made with each iteration. | ||
== Convex Relaxation == | |||
Convex relaxation involves transforming a non-convex optimization problem into a convex one by relaxing its constraints or objective function. This allows efficient algorithms for convex optimization to approximate solutions for the original problem. | |||
'''Original Problem''': | |||
<math>\min(f(x)) | |||
</math> subject to <math>g_i(x) \leq 0</math> <math>\bigl(i = 1,...,m\bigr)</math>, <math>h_j(x) = 0 </math> <math>\bigl(j = 1,...,p\bigr)</math> | |||
where <math>f(x), g_i(x), h_j(x)</math> are non-convex. | |||
'''Relaxation''': | |||
Reformulate <math>g_i(x)</math> and <math>h_j(x) </math> into convex constraints )<math>\bar{g_i(x)}</math> and <math>\bar{h_j(x)}</math> to create: | |||
<math>\min(f(x)) | |||
</math> ,subject to <math>\bar{g_i(x)} \leq 0</math>,<math>\bar{h_j(x)} = 0 </math> | |||
==Cutting Plane Methods== | ==Cutting Plane Methods== | ||
| Line 73: | Line 104: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
This new minimization formulation is now differentiable and easier to deal with, however it is only an approximation of the original equation which will become a better approximation as more constraints are added to the new model. | This new minimization formulation is now differentiable and easier to deal with, however it is only an approximation of the original equation which will become a better approximation as more constraints are added to the new model. | ||
==Illustrative Example== | ==Illustrative Example== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:18, 15 December 2024
Author: Kevin Afoakwah (ka475), Meghna Sen (ms3398) (ChemE 6800 Fall 2024)
Stewards: Nathan Preuss, Wei-Han Chen, Tianqi Xiao, Guoqing Hu
Background
Introduction
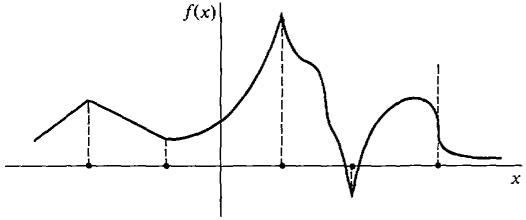
Non-differentiable optimization is a category of optimization that deals with objective that for a variety of reasons is non differentiable and thus non-convex. The functions in this class of optimization are generally non-smooth. These functions although continuous often contain sharp points or corners that do not allow for the solution of a tangent and are thus non-differentiable. In practice non-differentiable optimization encompasses a large variety of problems and a single one-size fits all solution is not applicable however solution is often reached through implementation of the subgradient method. Non-differentiable functions often arise in real world applications and commonly in the field of economics where cost functions often include sharp points. Early work in the optimization of non-differentiable functions was started by Soviet scientists Dubovitskii and Milyutin in the 1960's and led to continued research by Soviet Scientists. The subject has been a continued field of study since with different theories and methods being applied to solution in different cases.
Cost Functions
In many cases, particularly economics the cost function which is the objective function of an optimization problem is non-differentiable. These non-smooth cost functions may include discontinuities and discontinuous gradients and are often seen in discontinuous physical processes. Optimal solution of these cost functions is a matter of importance to economists but presents a variety of issues when using numerical methods thus leading to the need for special solution methods.
Solution Methods
Solution of differentiable problems and differentiable cost functions can in general forms be solved with gradient based analytical methods such as the Kuhn-Tucker model and through numerical methods such as steepest descent and conjugate gradient. However the introduction of non-differentiable points in the function invalidates these methods, steepest descent cannot be calculated for a vertical line. A common method for solution of a non-differentiable cost function is through transformation into a non-linear programming model where all of the of new functions involved are differentiable such that solution is now possible through ordinary means.
Subgradient Method
The subgradient method is an optimization technique used for minimizing non-smooth convex functions. It is particularly useful when the objective function is non-differentiable. Subgradients are almost identical to simple gradients since the convex functions are differentiable at any point, however, the key difference is in the step size when referring to the method of steepest descent. Non-differential function’s most optimal point might be a non-differential point and will not converge to zero like a simple gradient. Therefore, subgradients relax these step-size rules to find the appropriate optimal point by generalizing gradient descent and using minimization techniques.
Algorithm Steps:
Assumptions: The function is convex
- Initialization: Start with initial point x0 and step size t0
- Iterative Update: At each iteration k:
- Compute the subgradient gk of the function f(x) at the current point xk
- Update the current point using formulaFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [x_{k+1} = x_k + t_kg_k]}
- Update the step size tk according to a predefined rule
- Convergence Check: Repeat iteration updates until a stopping criterion is met. This can be when there is a maximum number of iterations, or a sufficiently small change in function value.
Simple Kink Case
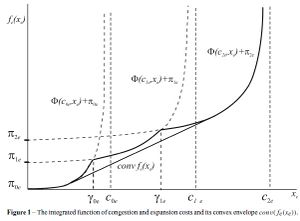
A common case of a non-differentiable function is the simple kink. The function is of the form:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Min \quad f(x) }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S.t. \quad x \in Q \subset R^n }
The function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) }
is non-differentiable because of several simple kinks which can be modeled by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \gamma [f_i(x)] = max\{0,f_i(x)\} \qquad i \in I }
If these simple kinks were removed the function would be differentiable across the entire domain. Some other types of non-differentiable objective functions can be modeled as simple kinks to allow the same type of solution.
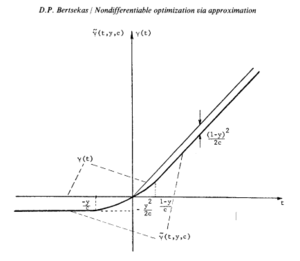
The approach to solution of the simple kink case is to approximate each of the non-differentiable kinks with a smooth function that will allow conventional solution to the entire problem. This requires that the kinks be the only factor that renders the function non-differentiable. A simple kink can be modeled by a two-parameter approximation,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{\gamma}[f(x), y, c] }
, of the simple kink Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \gamma [f(x)] }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{\gamma}[f(x), y, c] = \begin{cases} f(x) - (1-y)^2 /2c, & \text{if } (1-y)/c \le f(x), \\ yf(x) + \tfrac{1}{2}c[f(x)]^2, & \text{if } -y/c \le f(x) \le (1-y)/c \\ -y^2/2c, & \text{if } f(x) \le -y/c \end{cases} }
Where y and c are parameters with
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0 \le y \le 1, 0 < c }
Each kink Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \gamma_i }
will be replaced in the function with its two-parameter approximation such the new Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{f(x)} }
function is differentiable with the parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c >0 }
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0<y<1 }
. The solution can now be iteratively solved by adjusting the parameters c and y and solving the optimization problem
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Min \quad \tilde{f(x)} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s.t. \quad x \in Q \subset X }
A solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_k }
to the approximated objective function will be obtained. The problem is now resolved with an updated parameter for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c }
which is obtained by multiplying Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta c_k }
which Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = c_{k+1} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta > 0. \quad y_{k+1} }
can also be updated if necessary. And a new minimization carried out with the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k+1}
case. The procedure can be repeated until a value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) }
that is consistent with the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c }
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y }
parameters is reached.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon} -Subgradient Method
If the non-differentiable function is convex and subject to convex constraints then the use of the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon}
-Subgradient Method can be applied. This method is a descent algorithm which can be applied to minimization optimization problems given that they are convex.
With this method the constraints won't be considered explicitly but rather the objective function will be minimized to the value Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle + \infty }
.
This makes it such that the minimization of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g(.) }
over set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X }
is equal to finding the minimum of the extended real value function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = g(x) + \delta(x|X) }
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta(|X) }
is the indicator function of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X}
.
The solution will converge through a 4 step system, the basis of these steps lies a series of propositions which are further detailed in [1].
Step 1: Select a vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{\circ} }
such that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_{\circ}) < \infty }
, a scalar Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon_{\circ} > 0 }
and a scalar Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a, 0 < a < 1 }
.
Step 2: Given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_n, \quad \varepsilon_n > 0, }
set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon_{n+1} = a^k\varepsilon_n , }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k }
is the smallest non-negative integer such that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0 \not\in \delta_{\varepsilon_{n+1}}f(x^n) }
Step 3: Find a vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y_n }
such that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} sup \quad & \langle y_n , x^* \rangle < 0 \\ x^* \in \delta_{\varepsilon_{n+1}}f(x) & \\ \end{align} }
Step 4: Set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{n+1} = x_n + \lambda_n y_n, }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_n > 0 }
is such that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_n) - f(x_{n+1}) > \varepsilon_{n+1} }
Return to step 2 to iterate until convergence.
This method is not only guaranteed to converge but progress towards convergence is made with each iteration.
Convex Relaxation
Convex relaxation involves transforming a non-convex optimization problem into a convex one by relaxing its constraints or objective function. This allows efficient algorithms for convex optimization to approximate solutions for the original problem.
Original Problem:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \min(f(x)) } subject to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_i(x) \leq 0} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bigl(i = 1,...,m\bigr)} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_j(x) = 0 } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bigl(j = 1,...,p\bigr)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x), g_i(x), h_j(x)} are non-convex.
Relaxation:
Reformulate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_i(x)} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h_j(x) } into convex constraints )Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bar{g_i(x)}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bar{h_j(x)}} to create:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \min(f(x)) } ,subject to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bar{g_i(x)} \leq 0} ,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bar{h_j(x)} = 0 }
Cutting Plane Methods
Cutting planes were first utilized for the convergence of convex non-differentiable equations. The application of cutting planes will use the subgradient inequality to change the function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f }
by approximating it as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) \cong \tfrac{max}{i \in I} f(x_i) + \xi_i^T(x-x_i) }
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \xi_i^f , \quad i \in I }
are subgradients of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f }
at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_i, \quad i \in I }
. Thus, The original problem is now formulated as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tfrac{min}{x} \{ \tfrac{max}{i \in I} f(x_i) + \xi_i^T(x-x_i) \} }
Which is equivalent to the new problem
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Min \quad v }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s.t. \quad f(x_i) + \xi_i^T(x-x_i) \le v \quad \forall i \in I }
This new minimization formulation is now differentiable and easier to deal with, however it is only an approximation of the original equation which will become a better approximation as more constraints are added to the new model.
Illustrative Example
A simple example of non-differentiable optimization is approximation of a kink origination from an absolute value function. The simple function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f = |x| }
is an example of a function that while continuous for an infinite domain is non-differentiable at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = 0 }
due to the presence of a "kink" or point that will not allow for the solution of a tangent. Since the non-differentiable point of the function is known an approximation can be added to relax and smooth the function with parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t }
. This new approximation can be modeled
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{cases} -x & x \ge t, \\ \tfrac{x^2}{t} & -t \le x \le t, \\ x & x \ge t, \\ \end{cases} }
References
1. Bertsekas,D. Mitter, S. "A Descent Numerical Method for Optimization Problems with Nondifferentiable Cost Functionals*" Vol 11, No 4 of Siam Journal of Control, 1973.
2. Bertsekas, D. "Nondifferentiable Optimization Via Approximation" Vol 1, No 25 of Mathematical Programming Study 3, 1975.
3. Elhedhli, S. Goffin, J-L. Vial, J-P. "Nondifferentiable Optimization: Introduction, Applications and Algorithms" Encyclopedia of Optimization, 2000.