RMSProp: Difference between revisions
Jason Huang (talk | contribs) (Undo revision 1249 by Jason Huang (talk)) Tags: Replaced Undo |
Jason Huang (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
RMSProp, so call root mean square propagation, is an optimization algorithm/method dealing with Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for machine learning. It is also a currently developed algorithm compared to the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) algorithm, momentum method. And even one of the foundations of Adam algorithm development. | |||
It is an unpublished optimization algorithm, using the adaptive learning rate method, first proposed in the Coursera course [https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf “Neural Network for Machine Learning” lecture six] by Geoff Hinton. Astonished is that this informally revealed, an unpublished algorithm is intensely famous nowadays. | |||
==Theory and Methodology== | |||
'''Artificial Neural Network''' | |||
Artificial Neural Network can be regarded as the human brain and conscious center of Ariticial Intelligence(AI), presenting the imitation of what the mind will be when human thinking. Scientists are trying to build the concept of ANN close real neurons with their biological ‘parent’. | |||
[[File:Neuron.png|thumb|A single neuron presented as a mathematic function ]] | |||
<gallery> | |||
</gallery> | |||
And the function of neurons can be presented as: | |||
<math>f (x_{1},x_{2}) = max(0, w_{1} x_{1} + w_{2} x_{2}) </math> | |||
Where <math>x_{1},x_{2} </math> are two inputs numbers, and function <math>f (x_{1},x_{2}) </math> will takes these fixed inputs and create an output of single number. If <math>w_{1} x_{1} + w_{2} x_{2} </math> is greater than 0, the function will return this positive value, or return 0 otherwise. Therefore, the neural network can be replaced as a coupled mathematical function, and its output of a previous function can be used as the next function input. | |||
'''RProp''' | |||
RProp, or we call Resilient Back Propagation, is the widely used algorithm for supervised learning with multi-layered feed-forward networks in the past. Besides, its concepts is the foundation of RMSPRop development t. The derivatives equation of error function can be represented as: | |||
Revision as of 03:11, 19 November 2020
Author: Jason Huang (SysEn 6800 Fall 2020)
Steward: Allen Yang, Fengqi You
Introduction
RMSProp, so call root mean square propagation, is an optimization algorithm/method dealing with Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for machine learning. It is also a currently developed algorithm compared to the Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) algorithm, momentum method. And even one of the foundations of Adam algorithm development. It is an unpublished optimization algorithm, using the adaptive learning rate method, first proposed in the Coursera course “Neural Network for Machine Learning” lecture six by Geoff Hinton. Astonished is that this informally revealed, an unpublished algorithm is intensely famous nowadays.
Theory and Methodology
Artificial Neural Network
Artificial Neural Network can be regarded as the human brain and conscious center of Ariticial Intelligence(AI), presenting the imitation of what the mind will be when human thinking. Scientists are trying to build the concept of ANN close real neurons with their biological ‘parent’.
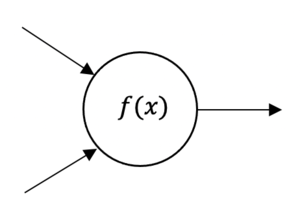
And the function of neurons can be presented as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f (x_{1},x_{2}) = max(0, w_{1} x_{1} + w_{2} x_{2}) }
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{1},x_{2} } are two inputs numbers, and function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f (x_{1},x_{2}) } will takes these fixed inputs and create an output of single number. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle w_{1} x_{1} + w_{2} x_{2} } is greater than 0, the function will return this positive value, or return 0 otherwise. Therefore, the neural network can be replaced as a coupled mathematical function, and its output of a previous function can be used as the next function input.
RProp
RProp, or we call Resilient Back Propagation, is the widely used algorithm for supervised learning with multi-layered feed-forward networks in the past. Besides, its concepts is the foundation of RMSPRop development t. The derivatives equation of error function can be represented as: