Quadratic assignment problem: Difference between revisions
NatashaRice (talk | contribs) (Finalized backboard problem) |
m (→Example) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Example == | == Example == | ||
Consider a set of 3 facilities and 3 locations that can house these facilities. | |||
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
Revision as of 15:27, 21 November 2020
Author: Thomas Kueny, Eric Miller, Natasha Rice, Joseph Szczerba, David Wittmann (SysEn 5800 Fall 2020)
Introduction
Theory, Methodology, and/or Algorithmic Discussions
Joe Szczerba and Tom Kueny to provide.
Example
Consider a set of 3 facilities and 3 locations that can house these facilities.
Applications
Natasha Rice and David Wittmann to provide.
The Backboard Wiring Problem
As the quadratic assignment problem is focused on minimizing the cost of traveling from one location to another, it is an ideal approach determining placement of components in many modern electronics. Leon Steinberg proposed a QAP solution optimize the layout of elements on a blackboard by minimizing the total amount of wiring required.
When defining the problem Steinberg states that we have a set of n elements
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E = \left \{ E_{1}, E_{2}, ... , E_{n}\right \}}
as well as a set of r points
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r \geq n}
In his paper he derives the below formula:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle min \sum_{1\leq i \leq j \leq n }^{} C_{ij}(d_{s(i)s(j))})}
represents the number of wires connecting components Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{i}}
and Failed to parse (Conversion error. Server ("https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_") reported: "Cannot get mml. Server problem."): {\displaystyle E_{i}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{s(i)s(j))}} is the length of wire needed to connect tow components if one is placed at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{\alpha}} and the other is placed at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{\beta}} . If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{\alpha}} has coordinates Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x_{\alpha}, y_{\alpha}, z_{\alpha})} then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{s(i)s(j))}} can be calculated by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{s(i)s(j))} = \surd(\bigl(x_{\alpha} - x_{\beta}\bigr)^{2} + \bigl(y_{\alpha} - y_{\beta}\bigr)^{2} + \bigl(z_{\alpha} - z_{\beta}\bigr)^{2}) }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s(x)} represents a particular placement of a component.
In his paper Steinberg a backboard with a 9 by 4 array, allowing for 36 potential positions for the 34 components that needed to be placed on the backboard. For the calculation he selected a random initial placement of s1 and chose a random family of 25 unconnected sets.
The initial placement of components is shown below:
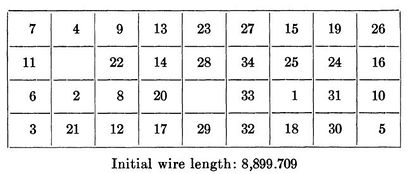
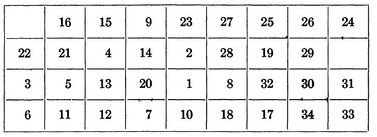
After the initial placement of elements it took an additional 35 iterations to get us to our final optimized backboard layout. Leading to a total of 59 iterations and a final wire length of 4,969.440.
Hospital Layout
Campus Building Arrangement
Molecular Confrontation Problem
Conclusion
References
- Alwalid N. Elshafei. Hospital Layout as a Quadratic Assignment Problem. Operational Research Quarterly (1970-1977). 1977;28(1):167. doi:10.2307/3008789
- Dickey JW, Hopkins JW. Campus building arrangement using topaz. Transportation Research. 6(1):59-68. doi:10.1016/0041-1647(72)90111-6
- Leon Steinberg. The Backboard Wiring Problem: A Placement Algorithm. SIAM Review. 1961;3(1):37.
- Phillips AT, Rosen JB. A quadratic assignment formulation of the molecular conformation problem. Journal of Global Optimization: An International Journal Dealing with Theoretical and Computational Aspects of Seeking Global Optima and Their Applications in Science, Management, and Engineer. 1994;4(2):229. doi:10.1007/bf01096724

