Conjugate gradient methods
Author: Alexandra Roberts, Anye Shi, Yue Sun (SYSEN 6800 Fall 2021)
Introduction
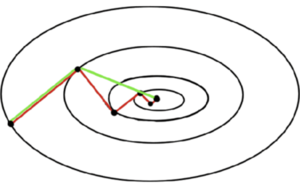
The conjugate gradient method (CG) was originally invented to minimize a quadratic function:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F(\textbf{x})=\frac{1}{2}\textbf{x}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{x}-\textbf{b}\textbf{x}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
is an Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \times n}
symmetric positive definite matrix, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}}
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{b}}
are Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n \times 1}
vectors.
The solution to the minimization problem is equivalent to solving the linear system, i.e. determining Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}}
when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla F(x) = 0}
, i.e. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}\textbf{x}-\textbf{b} = \textbf{0}}
.
The conjugate gradient method is often implemented as an iterative algorithm and can be considered as being between Newton’s method, a second-order method that incorporates Hessian and gradient, and the method of steepest descent, a first-order method that uses gradient. Newton's Method usually reduces the number of iterations needed, but the calculation of the Hessian matrix and its inverse increases the computation required for each iteration. Steepest descent takes repeated steps in the opposite direction of the gradient of the function at the current point. It often takes steps in the same direction as earlier ones, resulting in slow convergence (Figure 1). To avoid the high computational cost of Newton’s method and to accelerate the convergence rate of steepest descent, the conjugate gradient method was developed.
The idea of the CG method is to pick Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} orthogonal search directions first and, in each search direction, take exactly one step such that the step size is to the proposed solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} at that direction. The solution is reached after Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} steps [2] as, theoretically, the number of iterations needed by the CG method is equal to the number of different eigenvalues of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}} , i.e. at most Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} . This makes it attractive for large and sparse problems. The method can be used to solve least-squares problems and can also be generalized to a minimization method for general smooth functions [2].
Theory
The definition of A-conjugate direction
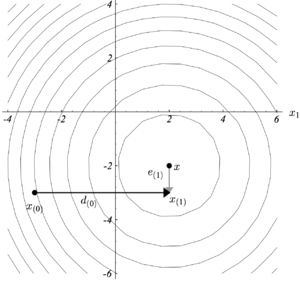
Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
be a symmetric positive definite matrix. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{ \textbf{d}_{0},\textbf{d}_{1},..., \textbf{d}_{n-1}\right\},\textbf{d}_{i} \in\textbf{R}^{n},\textbf{d}_{i} \neq 0}
are the search directional vectors that are orthogonal (conjugate) to each other with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_j = 0,\forall i\neq j}
. Note that if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}=0}
, any two vectors will be conjugated to each other. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}=\textbf{I}}
, conjugacy is equivalent to the conventional notion of orthogonality. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{ \textbf{d}_{0},\textbf{d}_{1},..., \textbf{d}_{n-1}\right\}}
are Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
-conjugated to each other, then the set of vectors Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{ \textbf{d}_{0},\textbf{d}_{1},..., \textbf{d}_{n-1}\right\}}
are linearly independent.
To illustrate the idea of conjugacy, the coordinate axes can be specified as search directions (Figure 2). The first step (horizontal) leads to the correct Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} coordinate of the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*} . The second step (vertical) will reach the correct Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y} coordinate of the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*} and then finish searching. We define that the error Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{e}_i = \textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_i} is a vector that indicates how far Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_i} is from the solution. The residual Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_i = \textbf{b} - \textbf{A}\textbf{x}_i} indicates how far Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{Ax}_i} is from the correct value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{b}} . Notice that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{e}_1} is orthogonal to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_0} . In general, for each step we choose a point
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_{i+1} = \textbf{x}_i + \alpha_i \textbf{d}_i}
.
To find the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_i} , use the fact that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{e}_i} should be orthogonal to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_i} so that no need to step in the direction of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_i} again in the later search. Using this condition, we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{e}_{i+1} = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{i}^{T}(\textbf{e}_{i} + \alpha_i\textbf{d}_i) = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_i = -\frac{\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{e}_{i}}{\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{d}_{i}}}
.
The motivation of A-conjugacy[4]
Notice from the above equation that the error Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e_i}
should be given first to get Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_i}
. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e_i}
is known, it would mean that the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
is already known, which is problematic. So, to compute Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_i}
without knowing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{e}_i}
, let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D=\left\{ \textbf{d}_{0},\textbf{d}_{1},..., \textbf{d}_{n-1}\right\}}
be a set of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
-conjugate vectors, then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D}
can be used as a basis and express the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^{\ast}}
to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla F(\textbf{x}) = \textbf{Ax} - \textbf{b} = \textbf{0}}
is:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^{\ast} = \sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\alpha _{i} \textbf{d}_{i}}
Then conduct transformation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
on both sides
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}\textbf{x}^{\ast} = \sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\alpha _{i} \textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}
Then multiply Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}}
on both sides
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{x}^{*} = \sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\alpha _{i} \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}
Because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{Ax} = \textbf{b}}
and the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
-conjugacy of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D}
, i.e. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i = 0, \forall k \neq i}
, the multiplication will cancel out all the terms except for term Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{b} = \alpha _{k} \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{k}}
So Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_k} can be obtained as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_{k}=\frac{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{b}}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{k}}}
Then the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
will be
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^{*}= \sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\alpha _{i}\textbf{d}_{i}=\sum_{i=0}^{n-1}\frac{\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{b}}{\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}\textbf{d}_{i}}
.
It takes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n}
steps to reach Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
. Additionally, because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
is a symmetric and positive-definite matrix, so the term Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}
defines an inner product and, therefore, no need to calculate the inversion of matrix Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
.
Conjugate Direction Theorem
To demonstrates that the above procedure does compute Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n}
steps, we introduce the conjugate direction theorem. Similar as the above, let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D=\left\{ \textbf{d}_{0},\textbf{d}_{1},..., \textbf{d}_{n-1}\right\}}
be a set of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
-conjugate vectors, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0 \in \textbf{R}^n}
be a random starting point. Then the theorem is as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_{k+1} = \textbf{x}_{k} + \alpha_{k} \textbf{d}_{k}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{k} = \textbf{b}- \textbf{A}\textbf{x}_{k}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_{k} = \frac{\textbf{g}_{k}^{T}\textbf{d}_{k}}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{k}} =\frac{(\textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_{k})^{T}\textbf{d}_{k}}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{k}}}
After Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n}
steps, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_n = \textbf{x}^*}
.
Proof:
The error Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e_0}
from the starting point to the solution can be formulated as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^* - \textbf{x}_0 = \alpha_0\textbf{d}_0 + \alpha_1\textbf{d}_1+...+\alpha_{n-1}\textbf{d}_{n-1}}
And the traversed steps from the starting point to the point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_k}
can be expressed as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_k - \textbf{x}_0 = \alpha_0\textbf{d}_0 + \alpha_1\textbf{d}_1+...+\alpha_{k-1}\textbf{d}_{k-1}}
The residual term from the solution point to the point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_k}
can be expressed as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_k = \textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_k = \textbf{A}\textbf{x}^{*}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_k = \textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^{*}-\textbf{x}_k)}
Therefore, the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_k}
is as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_0) = \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\alpha_0\textbf{d}_0+\alpha_1\textbf{d}_1 +...+\alpha_{n-1}\textbf{d}_{n-1}) = \alpha_k\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_{k} = \frac{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_0)}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k}}
But, still, the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
has to be known first to calculate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_k}
. So, the following manipulations can get rid of using Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}^*}
in the above expression:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}_k-\textbf{x}_0) = \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\alpha_0\textbf{d}_0+\alpha_1\textbf{d}_1 +...+\alpha_{k-1}\textbf{d}_{k-1} ) = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_0) = \textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_k + \textbf{x}_k - \textbf{x}_0) =\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_k)}
Therefore
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_k = \frac{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_0)}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k} = \frac{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}(\textbf{x}^*-\textbf{x}_k)}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k}=\frac{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{g}_k}{\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k}}
The conjugate gradient method
The conjugate gradient method is a conjugate direction method in which selected successive direction vectors are treated as a conjugate version of the successive gradients obtained while the method progresses. The conjugate directions are not specified beforehand but rather are determined sequentially at each step of the iteration [4]. If the conjugate vectors are carefully chosen, then not all the conjugate vectors may be needed to obtain the solution. Therefore, the conjugate gradient method is regarded as an iterative method. This also allows approximate solutions to systems where n is so large that the direct method requires too much time [2].
Derivation of Algorithm[2]
Given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D=\left\{ \textbf{d}_{1},\textbf{d}_{2},..., \textbf{d}_{n}\right\}} be a set of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}} -conjugate vectors, then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F(\textbf{x}_0 +\alpha_1\textbf{d}_1 + \alpha_2\textbf{d}_2+...+\alpha_{n}\textbf{d}_{n})} can be minimized by stepping from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0} along Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_1} to the minimum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_1} , stepping from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_1} along Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_2} to the minimum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_2} , etc. And let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0 \in \textbf{R}_n} be randomly chosen, then the algorithm is the following:
|
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underline{Algo\;1:Pick\;\left\{ \textbf{d}_{1},\textbf{d}_{2},..., \textbf{d}_{n}\right\}\;mutually\;\textbf{A}-conjugate,\;and\;start\;from\;a\;random\;\textbf{x}_0}} Set a starting point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0} Set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k = 1} Set the maximum iteration Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} While Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k \le n} :
End while Return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_n} |
Here Alg 1 is with a particular choice of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{ \textbf{d}_{1},\textbf{d}_{2},..., \textbf{d}_{n}\right\}}
. Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{k} = \textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_{k}}
be the residual (equivalent to the negative of the gradient) at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_k}
. A practical way to enforce this is by requiring that the next search direction be built out of the current gradient and all previous search directions. The CG method picks Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k+1}}
as the component of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_k}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}}
-conjugate to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{ \textbf{d}_{1},\textbf{d}_{2},..., \textbf{d}_{k}\right\}}
:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k+1} = \textbf{g}_k-\sum_{i=1}^{k}\frac{\textbf{g}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}{\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i}}\textbf{d}_i}
As Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{i} = 0} , for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i = 1,...,k} , giving the following CG algorithm:
|
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underline{Alg\;2:\;Revised\;algorithm\;from\;Alg\;1\;without\;particular\;choice\;of\;D}} Set a starting point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0} Set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k = 1} Set the maximum iteration Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} While Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k \leq n} :
Return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_n} |
The formulas in the Alg 2 can be simplified as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_i = \textbf{x}_{i-1}+\alpha_i\textbf{d}_i}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_i = \textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_{i-1}-\alpha_i\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_i = \textbf{g}_{i-1}-\alpha_i\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_i} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_i} can be simplified by multiplying the above gradient formula by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_i} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i-1}} as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i}^{T}\textbf{g}_i = -\alpha_i\textbf{g}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i-1}^{T}\textbf{g}_{i-1} = \alpha_i\textbf{g}_{i-1}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
As Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i-1} = \textbf{d}_i+\beta_i\textbf{d}_{i-1}}
, so we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i-1}^{T}\textbf{g}_{i-1} = \alpha_i\textbf{g}_{i-1}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i=\alpha_i\textbf{d}_{i}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
Therefore
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_{i+1} = -\frac{\textbf{g}_{i}^{T}\textbf{g}_{i}}{\textbf{g}_{i-1}^{T}\textbf{g}_{i-1}}}
This gives the following simplified version of Alg 2:
Alg 3: From a random Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_0}
, and set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_0 = \textbf{b} - \textbf{A}\textbf{x}_0}
,
For k = 1 to n
{
- if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{k-1} = 0}
return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_{k-1}}
;
- if (k > 1) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_k = -(\textbf{g}_{k-1}^{T}\textbf{g}_{k-1})/(\textbf{g}_{k-2}^{T}\textbf{g}_{k-2})}
;
- if (k = 1) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_k = \textbf{g}_0}
;
- else Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_{k} = \textbf{g}_{k-1}-\beta_k\textbf{d}_{k-1}}
;
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_k=(\textbf{g}_{k-1}^{T}\textbf{g}_{k-1})/(\textbf{d}_{k}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_k)}
;
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_k = \textbf{x}_{i-1} + \alpha_i\textbf{d}_i}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{i}=\textbf{g}_{i-1}-\alpha_i\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i}
;
}
Return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_n}
Numerical example
Consider the linear system Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}\textbf{x} = \textbf{b}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}\textbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 1 \\1 & 8 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}x_{1} \\x_{2}\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}3 \\2\end{bmatrix} = \textbf{b}}
.
The initial starting point is set to be
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_{0} = \begin{bmatrix}2 \\1\end{bmatrix}}
.
Implement the conjugate gradient method to approximate the solution to the system.
Solution:
The exact solution is given below for later reference:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_{*} = \begin{bmatrix}22/39 \\7/39\end{bmatrix}\approx \begin{bmatrix}0.5641\\0.1794\end{bmatrix}}
.
Step 1:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{0}=\textbf{b}-\textbf{A}\textbf{x}_0 = \begin{bmatrix}3 \\2\end{bmatrix}-\begin{bmatrix}5 &1 \\1& 8\\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}2\\1\end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix}-8 \\-8\end{bmatrix}= \textbf{d}_1}
Step 2:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_1 = \frac{\textbf{g}_{0}^{T}\textbf{g}_{0}}{\textbf{d}_{1}^{T}\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_1}=\frac{\begin{bmatrix}-8 &-8 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-8 \\-8\end{bmatrix}}{\begin{bmatrix}-8 &-8 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}5 &1 \\1& 8 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-8 \\-8\end{bmatrix}}=\frac{2}{15}}
Step 3:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_1 = \textbf{x}_{0} + \alpha_{1}\textbf{d}_{1}=\begin{bmatrix}2\\1\end{bmatrix}+\frac{2}{15}\begin{bmatrix}-8\\-8\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}0.9333 \\-0.0667\end{bmatrix}}
Step 4:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{g}_{1}=\textbf{g}_{0}-\alpha_1\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_1 = \begin{bmatrix}-8\\-8 \end{bmatrix}-\frac{2}{15}\begin{bmatrix}5&1\\1&8\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-8\\-8\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}-1.6\\1.6\end{bmatrix}}
Step 5:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_2 =-\frac{\textbf{g}_{1}^T\textbf{g}_{1}}{{\textbf{g}_{0}^T\textbf{g}_{0}}}=- \frac{\begin{bmatrix}-1.6&1.6\\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-1.6 \\1.6\end{bmatrix}}{\begin{bmatrix}-8 &-8\\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-8 \\-8\end{bmatrix}}= -0.04}
Step 6:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{d}_2 = \textbf{g}_1 - \beta_2\textbf{d}_1=\begin{bmatrix}-1.6\\1.6\end{bmatrix}+0.04\begin{bmatrix}-8\\-8\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}-1.92 \\1.28\end{bmatrix}}
Step 7:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_2 =\frac{\textbf{g}_{1}^T\textbf{g}_{1}}{{\textbf{d}_{2}^T\textbf{A}\textbf{d}_{2}}}=\frac{\begin{bmatrix}-1.6 &1.6\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-1.6\\1.6\end{bmatrix}}{\begin{bmatrix}-1.92&1.28\\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}5 &1 \\1& 8 \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}-1.92\\1.28\end{bmatrix}}=0.1923}
Step 8:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_2 = \textbf{x}_{1} +\alpha_{2}\textbf{d}_{2}=\begin{bmatrix}0.9333\\-0.0667\end{bmatrix}+0.1923\begin{bmatrix}-1.92\\1.28\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}0.5641 \\0.1794\end{bmatrix}}
Therefore, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x}_2}
is the approximation result of the system.
Application
Conjugate gradient methods have often been used to solve a wide variety of numerical problems, including linear and nonlinear algebraic equations, eigenvalue problems and minimization problems. These applications have been similar in that they involve large numbers of variables or dimensions. In these circumstances any method of solution which involves storing a full matrix of this large order, becomes inapplicable. Thus recourse to the conjugate gradient method may be the only alternative [5]. Here we show an example of image reconstruction.
Iterative image reconstruction
The conjugate gradient method is used to solve for the update in iterative image reconstruction problems. For example, in the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast known as quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), the reconstructed image Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi}
is iteratively solved for from magnetic field data Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{b}}
by the relation[6]
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{b}=\textbf{D}\chi}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D}
is the matrix expressing convolution with the dipole kernel in the Fourier domain. Given that the problem is ill-posed, a physical prior is used in the reconstruction, which is framed as a constrained L1 norm minimization
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle min_{\chi}\left\| f(\chi)\right\|_1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s.t. \left\| g(\chi)-c\right\|_{2}^{2}}
A detailed treatment of the function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(\chi)}
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g(\chi)}
can be found at [6]. This problem can be expressed as an unconstrained minimization problem via the Lagrange Multiplier Method
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle min_{\chi,\lambda}E(\chi,\lambda)}
Where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E(\chi,\lambda)\equiv \left\| f(\chi)\right\|_1+\lambda (\left\| g(\chi)-c\right\|_{2}^{2}-\varepsilon)}
The first-order conditions require Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla_{\chi}E(\chi,\lambda)=0}
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla_{\lambda}E(\chi,\lambda)=0}
. These conditions result in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla_{\chi}f(\chi)+\nabla_{\chi}g(\chi) - \tilde{c}=0}
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\| g(\chi)-c\right\|_{2}^{2}\approx \varepsilon }
, respectively. The update can be solved for
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla_{\chi}f(\chi)+\nabla_{\chi}g(\chi) - \tilde{c}=L(\chi)\chi-\tilde{c}=0}
via fixed point iteration [6].
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{n+1}=L^{-1}(\chi^n)\tilde{c}}
And expressed as the quasi-Newton problem, more robust to round-off error [6]
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{n+1}=\chi_n - L^{-1}(\chi_n)\nabla E(\chi_n,\lambda)}
Which is solved with the CG method until the residual Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\|\chi_{n+1}-\chi\right\|_2/\left\|\chi_n\right\|_2\leq \theta }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta}
is a specified tolerance, such as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 10^{-2}}
.
Conclusion
The conjugate gradient method was invented to avoid the high computational cost of Newton’s method and to accelerate the convergence rate of steepest descent. As an iterative method, each step only requires Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}\textbf{d}_i} multiplication free from the storage of matrix Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{A}} . And selected direction vectors are treated as a conjugate version of the successive gradients obtained while the method progresses. So it monotonically improves approximations Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{x} _k} to the exact solution and may reach the required tolerance after a relatively small (compared to the problem size) number of iterations in the absence of round-off error, which makes it widely used for solving large and sparse problems.
Reference
- ↑ Refsnæs, Runar Heggelien. “A Brief introduction to the conjugate gradient method.” (2009).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 W. Stuetzle, “The Conjugate Gradient Method.” 2001. [Online]. Available: https://sites.stat.washington.edu/wxs/Stat538-w03/conjugate-gradients.pdf
- ↑ Jonathan Shewchuk, “An Introduction to the Conjugate Gradient Method Without the Agonizing Pain,” 1994.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 A. Singh and P. Ravikumar, “Conjugate Gradient Descent.” 2012. [Online]. Available: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~pradeepr/convexopt/Lecture_Slides/conjugate_direction_methods.pdf
- ↑ R. Fletcher, “Conjugate gradient methods for indefinite systems,” in Numerical Analysis, Berlin, Heidelberg, 1976, pp. 73–89. doi: 10.1007/BFb0080116.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 J. Liu et al., “Morphology enabled dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping using structural consistency between the magnitude image and the susceptibility map,” NeuroImage, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 2560–2568, Feb. 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.082.