Stochastic dynamic programming
Authors: Bo Yuan, Ali Amadeh, Max Greenberg, Raquel Sarabia Soto and Claudia Valero De la Flor (CHEME/SYSEN 6800, Fall 2021)
Introduction
In real-world decision-making problems, uncertainty is very frequently a non-negligible factor. Uncertainty may exist in the estimation of model parameters, in input or output signals, in extraneous disturbances, or in general and unaccounted-for mismatch between a model and the real system it represents. However, such decision problems are still solvable, and stochastic dynamic programming in particular serves as a powerful tool to derive optimal decision policies despite the form of uncertainty present.
Stochastic dynamic programming as a method was first described in the 1957 white paper “A Markovian Decision Process” written by Richard Bellman for the Rand Corporation. Bellman’s formulation of the problem was intended to address a general industrial equipment replacement problem, in which machinery used to produce a given item has some time-dependent probability of producing defective items or breaking down entirely. Since these probability distribution functions of failure over time are assumed invariant and the probability of failure at time t is independent of past realizations, the Markovian decision process Bellman describes represents a comparatively simple and well-behaved stochastic dynamic problem. However, modern stochastic dynamic programming has developed into an even more versatile tool.
Today, stochastic dynamic programming formulations have been proposed for a wide range of practical decision-making problems. These include, but are not limited to, water reservoir management [1], water quality management [2], production planning [3], breeding policy in livestock herds [4], energy allocation and reserve management [5], drought mitigation [6], fuel consumption optimization for hybrid vehicles [7], and management of land for endangered species [8].
Theory, methodology and algorithm discussion
Theory
Stochastic dynamic programming combines stochastic programming and dynamic programming. Therefore, to understand better what it is, it is better first to give two definitions [9]:
- Stochastic programming. Unlike in a deterministic problem, where a decision’s outcome is only determined by the decision itself and all the parameters are known, in stochastic programming there is uncertainty and the decision results in a distribution of transformations.
- Dynamic programming. It is an optimization method that consists in dividing a complex problem into easier subprobems and solving them recursively to find the optimal sub-solutions which lead to the complex problem optima.
In any stochastic dynamic programming problem, we must define the following concepts [10]:
- Policy, which is the set of rules used to make a decision.
- Initial vector, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p\in\ D} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle D} is a finite closed region.
- Choice made, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q\in\ S} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S} is a set of possible choices.
- Stochastic vector, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} .
- Distribution function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_q(p,z)} , associated with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} and dependent on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} .
- Return, which is the expected value of the function after the final stage.
In a stochastic dynamic programming problem, we assume that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} is known after the decision of stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n-1} has been made and before the decision of stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} has to be made.
Methodology and algorithm
Formulation in a continuous state space
First, we define the N-stage return obtained using the optimal policy and starting with vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_N\left(p\right)=\max{R\left(p_N\right)}}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R\left(p_N\right)} is the function of the final state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_N} .
Second, we define the initial transformation as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_q} , and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} , as the state resulting from it. The return after Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N-1} stages will be Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_{N-1}(z)} using the optimal policy. Therefore, we can formulate the expected return due to the initial choice made in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_q} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int_{z\in D}{f_{N-1}\left(z\right)dG_q(p,z)}}
Having defined that, the recurrence relation can be expressed as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_N\left(p\right)=\max{\ \int_{z\in D}{f_{N-1}\left(z\right)\ dG_q\left(p,z\right)\ }}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N\geq2}
With:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_1\left(p\right)=\max{\ \ \int_{z\in D}{R\left(z\right)dG_q(p,z)}}}
Formulation in a discrete state space
The continuous formulation presented takes the following form in a discrete state space. Let the state in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} be Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i} . Under action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} , the system transitions from state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i} in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} to state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j} in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n+1} with probability Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{ij}(a)} . The maximum expected return in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_n\left(i\right)=\max{\left[R\left(i,a\right)+\sum_{j}{P_{ij}\left(a\right)V_{n+1}\left(j\right)}\right]}}
which gives the recurrence relation that is needed in any dynamic programming model.
The formulations presented are very general and, depending on the problem characteristics, different models can be developed. For this reason, we present the algorithm of a specific model as example: a model for Approximate Dynamic Programming (ADP).
Approximate Dynamic Programming (ADP)
Approximate dynamic programming (ADP) is an algorithm strategy for solving complex problems that can be stochastic. Since the topic of this page is Stochastic Dynamic Programming, we will discuss ADP from this perspective.
To develop the ADP algorithm, we present the Bellman’s equation using the expectation form.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_t\left(s\right)=max\ \left(C\left(S_t,\ x_t\right)+\gamma\ E\ \left\{V_{t+1}\left(S_{t+1}\right)|S_{t=s}\right\}\right)\ }
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{t+1}=S^M\left(S_t,\ x_t,\ W_{t+1}\right)} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t=X^\pi\left(S_t\right)} .
The variables used and their meanings are the following:
- State of the system, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t}
- Function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X^\pi\left(S_t\right)} . It represents the policy to make a decision
- Transition function, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S^M} . It describes the transition from state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t} to state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{t+1}} .
- Action taken in state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t}
- Information observed after taking action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle W_{t+1}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_t\left(s\right)} gives the expected value of being in state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t} at time Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} and making a decision following the optimal policy.
The goal of ADP is to replace the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_t\left(S_t\right)} with a statistical approximation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t} . Therefore, after iteration Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n-1} , we have an approximation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t^{n-1}\left(S_t\right)} . Another feature of ADP is that it steps forward in time. To go from one iteration to the following, we define our decision function as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X^\pi\left(S_t^n\right)=max\ \left(C\left(S_t^n,\ x_t\right)+\gamma\ E\ \left\{{\bar{V}}_{t+1}^{n-1}\left(S_{t+1}\right)|S_t^n\right\}\right)\ }
Next, we define Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t^n} as the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t} that solves this problem and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\hat{v}}_t^n} , as the estimate value of being in state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t^n} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\hat{v}}_t^n=C\left(S_t^n,\ x_t^n\right)+\gamma\ E\ \left\{{\bar{V}}_{t+1}^{n-1}\left(S_{t+1}\right)|\ S_t\right\}}
Finally, using the approximation lookup table, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t\left(s\right)} is defined. In a lookup approximation, for each state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s} we have a Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t(s)} that gives an approximated value of being in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t^n\left(S_t^n\right)=\left(1-\alpha_{n-1}\right){\bar{V}}_t^{n-1}\left(S_t^n\right)+\alpha_{n-1}{\hat{v}}_t^n} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha_{n-1}} is known as a stepsize
Therefore, a generic ADP algorithm applied to stochastic dynamic programming can be summarized as [11]:
1. We initialize Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t^0\left(S_t\right)} for all states Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t} , and we choose an initial state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_o^1} and set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=1} .
2. For t=0,1,2.., we have to solve:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\hat{v}}_t^n=C\left(S_t^n,\ x_t^n\right)+\gamma\ E\ \left\{{\bar{V}}_{t+1}^{n-1}\left(S_{t+1}\right)|\ S_t\right\}}
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_y=S_t^n} : Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t^n\left(S_t^n\right)=\left(1-\alpha_{n-1}\right){\bar{V}}_t^{n-1}\left(S_t^n\right)+\alpha_{n-1}{\hat{v}}_t^n}
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_t\neq\ S_t^n} : Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\bar{V}}_t^{n-1}\left(S_t\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{t+1}^n=S^M\left(S_t^n,\ x_t^n,\ W_{t+1}\left(w^n\right)\right)}
3. Set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=n+1} as long as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n<N} .
Numerical examples
Gamblling example
We have 4 chips, and we want to bet them to maximize the probability of ending with 8 chips after a maximum of 4 bets. In each bet, we can bet as many chips as we have. The probability of losing is 0.4 (where we lose every chip we have bet) and the probability of wining is 0.6 (where we get twice the number of chips we have bet).
Solution
The stages of this problem are the 4 bets we can make (represented by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} ), where we decide how many chips to bet (action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k} ). The state (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s} ) are the number of chips we have before making a bet in each stage.
Bet 4, State s:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{4}(s)=\{0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}, \quad s=0,1, \ldots, 8}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s<4}
, obviously, it does not matter whether to bet or not as there is no chance we can have eight chips at the end.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=4: f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3,4}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{4}(4)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(4)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{4}(4)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(3)=0 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{4}(4)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(2)=0 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{4}(4)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(1)=0 \\ k=4 \rightarrow f_{4}(4)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(0)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(4)=0.6, k^{*}=4}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=5: f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{4}(5)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(5)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{4}(5)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(4)=0 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{4}(5)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(3)=0 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{4}(5)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(0)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(5)=0.6, k^{*}=3}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=6: f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{4}(6)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(6)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{4}(6)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(5)=0 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{4}(6)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(4)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(6)=0.6, k^{*}=2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=7: f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{4}(7)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(7)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{4}(7)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(6)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(7)=0.6, k^{*}=1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=8: f_{4}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0}\left\{0.6 f_{5}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{k=0 \rightarrow f_{4}(8)=0.6 f_{5}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{5}^{*}(8)=1\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(8)=1, k^{*}=0}
Bet 3, State s:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{3}(s)=\{0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}, \quad s=0,1, \ldots, 8}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s<2}
, obviously, it does not matter whether to bet or not as there is no chance we can have eight chips at the end.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=2: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(2)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(2)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(2)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(2)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(3)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(1)=0 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{3}(2)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(0)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(2)=0.36, k^{*}=2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=3: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(3)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(3)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(3)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(3)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(2)=0.36 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{3}(3)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(1)=0.36 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{3}(3)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(0)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(3)=0.36, k^{*}=1,2,3}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=4: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3,4}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{l} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(4)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(4)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(4)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(3)=0.36 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{3}(4)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(2)=0.36 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{3}(4)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(1)=0.36 \\ k=4 \rightarrow f_{3}(4)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(0)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(4)=0.6, k^{*}=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=5: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(5)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(5)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(5)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(4)=0.6 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{3}(5)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(3)=0.36 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{3}(5)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(2)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(5)=0.6, k^{*}=0,1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=6: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{l} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(6)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(6)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(6)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(5)=0.6 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{3}(6)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(4)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(6)=0.6, k^{*}=0,1,2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=7: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{l} k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(7)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(7)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{3}(7)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(1)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(6)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{3}^{*}(7)=0.6, k^{*}=0,1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=8: f_{3}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0}\left\{0.6 f_{4}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{k=0 \rightarrow f_{3}(8)=0.6 f_{4}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{4}^{*}(8)=1\right\} \rightarrow f_{4}^{*}(8)=1, k^{*}=0}
Bet 2, State s:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{2}(s)=\{0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_{2}^{*}(s)=\underset{k=0,1, \ldots, \min \{s, 8-s\}}{\max }\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}, \quad s=0,1, \ldots, 8}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=0: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(0)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(0)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=1\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(0)=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=1: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(1)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(1)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(1)=0 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(1)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(2)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=0.216 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(1)=0.216, k^{*}=1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=2: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(2)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(2)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(2)=0.36 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(2)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(3)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(1)=0.216 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{2}(2)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(2)=0.36, k^{*}=0,2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=3: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(3)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(3)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(3)=0.36 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(3)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(2)=0.504 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{2}(3)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(1)=0.36 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{2}(3)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=0.36 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(3)=0.504, k^{*}=1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=4: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3,4}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(4)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(4)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(4)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(3)=0.504 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{2}(4)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(2)=0.504 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{2}(4)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(1)=0.36 \\ k=4 \rightarrow f_{2}(4)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(4)=0.6, k^{*}=0,4}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=5: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(5)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(5)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(5)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(4)=0.6 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{2}(5)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(3)=0.504 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{2}(5)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(2)=0.744 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(5)=0.744, k^{*}=3}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=6: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(6)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(6)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(6)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(5)=0.6 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{2}(6)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(4)=0.84 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(6)=0.84, k^{*}=2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=7: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{l} k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(1)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(7)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{2}(1)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(0)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(7)=0.6, k^{*}=0,1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s=8: f_{2}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0}\left\{0.6 f_{3}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(s-k)\right\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{k=0 \rightarrow f_{2}(8)=0.6 f_{3}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{3}^{*}(8)=1\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(8)=1, k^{*}=0}
Bet 1, State s:
For this bet, we know that we have 4 chips, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s_{1}=4}
:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U_{1}(s)=\{0,1, \ldots, 4\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_{1}^{*}(s)=\max _{k=0,1,2,3,4}\left\{0.6 f_{2}^{*}(s+k)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(s-k)\right\}, \quad s=4}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\{\begin{array}{c} k=0 \rightarrow f_{1}(4)=0.6 f_{2}^{*}(4)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(4)=0.6 \\ k=1 \rightarrow f_{1}(4)=0.6 f_{2}^{*}(5)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(3)=0.648 \\ k=2 \rightarrow f_{1}(4)=0.6 f_{2}^{*}(6)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(2)=0.648 \\ k=3 \rightarrow f_{1}(4)=0.6 f_{2}^{*}(7)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(1)=0.4464 \\ k=4 \rightarrow f_{1}(4)=0.6 f_{2}^{*}(8)+0.4 f_{2}^{*}(0)=0.6 \end{array}\right\} \rightarrow f_{2}^{*}(3)=0.648, k^{*}=1,2}
The probability of having eight chips is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0.648}
, and the sequence of optimal actions depends on not only the initial state, but also the disturbance (win/lose)
Applications: Problems
A stock-option model
This model was created to maximize the expected profit that we can obtain in N days (stages) from selling/buying stocks. This is considered a finite-stage model because we know in advance for how many days are we calculating the expected profit.
First, we define the stock price on the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k} th day Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (k\geq1)} as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_k} . We assume the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{k+1}=S_k+X_{k+1}=S_0+\sum_{i=1}^{k+1}X_i}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X_1,\ X_2,} … are independent of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_0} and between them, and identically distributed with distribution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F} .
Second, we also assume that we have the chance to buy a stock at a fixed price Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c} and this stock can be sold at price Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s} . We then define Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_n} as the maximal expected profit, and it satisfies the following optimality equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_n\left(s\right)=\max{\ \ [}s-c,\ \int{V_{n-1}\left(s+x\right)dF\left(x\right)}\ ]}
And the boundary condition is the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_0\left(s\right)=\max{\ \left(s-c,\ 0\right)}}
General gambling problem
Consider an unfair coin flip game where the probability of the coin landing on heads is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} and the probability of landing in tails is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} , and the game is each you flip head you win the amount you bet and each time you flip tails you lose the amount you bet as well. A gambler starts with a certain amount of money, cannot bet more money than he has and can play a limited number of games (the bet must be nonnegative). Our goal is to maximize the logarithm of his expected payout by using an optimal betting strategy. To find this we will use stochastic dynamic programming. Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} be the number of bets, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} be the amount of money we have on each step, α the percentage of our money that we will bet, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p} the probability of winning and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q} the probability of losing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (q=1-p)} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{n}(x)=\max _{0 \leq \alpha \leq 1}\left[p V_{n-1}(x+\alpha x)+q V_{n-1}(x-\alpha x)\right]}
With the boundary condition:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{0}(x)=\ln (x)}
For the first bet:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{aligned} &V_{1}(x)=\max _{0 \leq \alpha \leq 1}[p \ln (x+x \alpha)+q \ln (x-x \alpha)]=\max _{0 \leq \alpha \leq 1}[p \ln (1+\alpha)+q \ln (1-\alpha)]+\ln (x) \end{aligned}}
The maximum of the previous equation is obtained at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha=p-q} , so:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{1}(x)=C+\ln (x)}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C=\ln (2)+p \ln (p)+q \ln (q)}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=2} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{1}(x)=\max _{0 \leq \alpha \leq 1}[p \ln (x+x \alpha)+q \ln (x-x \alpha)]+C}
Once again, the optimal bet will be Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha=p-q} , so:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{2}(x)=2 C+\ln (x)}
It can be easily shown using induction that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{n}(x)=n C+\ln (x)}
Being always the best bet Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha=p-q} .
Secretary problem
Suppose that we are to employ one secretary from N unknown candidates whom we can sequentially see and tell if the new secretary has a higher value than the ones already seen. The conditions are:
- We can see each secretary only once
- In each stage, we can
- accept that secretary and the selection process will stop
- reject that secretary and observe the next one without being able to go back to it.
- For each candidate, we can measure if he/she is better than those previously seen.
Our goal is to develop a process to maximize the probability of employing the best secretary.
In each stage, we have 4 possible states:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{1}} if the secretary is already employed and is the best we have seen so far
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{0}} if the secretary is already employed and is not the best we have seen so far
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1} if the secretary is not yet employed, and the candidate we are seeing is the best we have seen so far
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0} if the secretary is not yet employed, and the candidate we are seeing is not the best we have seen so far
Also, in each stage, we can make different decisions:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} : accept (employ) the candidate we are seeing
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} : reject the candidate we are seeing
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} if we do nothing
Obviously, decisions “Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} ” and “Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} ” can be made only if the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (x)} is different from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{1}} or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{0}} . Thus, the set of allowable actions Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (U(x))} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle U(x)= \begin{cases}\{a, r\}, & \text { if } x \neq \lambda_{1} \text { or } x \neq \lambda_{0} \\ & \{n\}, \text { otherwise }\end{cases}}
It goes without saying that if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0} , we will always pass and reject the candidate.
Denoting each stage by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} , we know that the reward that can be obtained in each stage before the final stage is zero regardless of the state and the action taken. Thus, we can write:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_{t}(x, u)=0, \forall t=1, \ldots, T-1}
In the final stage, if the best secretary has been already employed or if the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N^{th}} secretary is the best we have seen so far, the reward is equal to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1} , otherwise, the reward is equal to zero. Hence, we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_{N}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{c} 1, x=\lambda_{1} \\ 0, x=\lambda_{0} \\ 1, x=1 \\ 0, x=0 \end{array}\right.}
The state transition probability matrix in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} under action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle u} can be defined as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{i j}^{t}(u)=P_{r}\left(x_{t+1}=j \mid x_{t}=i, u_{t}=u\right)}
Now, we can start formulating the Stochastic Dynamic Programming problem. In stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N} , we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{N}^{*}(x)=g_{N}(x)= \begin{cases}1, & x=\lambda_{1} \text { or } x=1 \\ 0, & x=\lambda_{0} \text { or } x=0\end{cases}}
For stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t<T} , the value function depends on the state. For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t}=\lambda_{0}} , Hence, the optimal value function under the only possible action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}\left(\lambda_{0}\right)=0}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t}=\lambda_{1}} , the next state can be either Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1}=\lambda_{1}} with probability Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{t}{t+1}} or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{t+1}=\lambda_{0}} with probability Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{t+1}} . Hence, the optimal value function under the only possible action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}\left(\lambda_{1}\right)=E\left\{V_{t+1}^{*}\left(x_{t+1}^{n}\right)\right\}=\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}\left(\lambda_{1}\right)+\frac{1}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}\left(\lambda_{0}\right)=\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}\left(\lambda_{1}\right)=}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{t}{t+1}\left(\frac{t+1}{t+2}\right) \ldots\left(\frac{N-1}{N}\right) V_{N}^{*}\left(\lambda_{1}\right)=\frac{t}{N}}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t}=0} , the next state can be either Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1}=0} with probability Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{t}{t+1}} or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{t+1}=1} with probability Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{t+1}} . Hence, the optimal value function under the only possible action Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)=E\left\{V_{t+1}^{*}\left(x_{t+1}^{r}\right)\right\}=\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(0)+\frac{1}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(1)}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t}=1} , the next state can be either Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1}=\lambda_{1}} or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1}=0} . The optimal value function under the two possible actions Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{aligned} V_{t}^{*}(1) &=\max \left\{E\left\{V_{t+1}^{*}\left(x_{t+1}^{a}\right)\right\}, E\left\{V_{t+1}^{*}\left(x_{t+1}^{r}\right)\right\}\right\}=\max \left\{\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}\left(\lambda_{1}\right), V_{t}^{*}(0)\right\} \\ &=\max \left\{\frac{t}{N}, V_{t}^{*}(0)\right\} \end{aligned}}
Thus, the optimal action policy in stage Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} and at each state can be written as follows:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu_{t}^{*}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{c} a, \quad x_{t}=1, \frac{t}{N} \geq V_{t}^{*}(0) \\ r, \quad x_{t}=1, \frac{t}{N}<V_{t}^{*}(0) \\ r, \quad x_{t}=0 \\ n, \quad x_{t}=\lambda_{1} \text { or } x_{t}=\lambda_{0} \end{array}\right.}
It can be easily shown that the optimal value functions at state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t}=0} are monotonically non-increasing in t meaning:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0) \geq V_{t+1}^{*}(0), \forall t}
The monotonicity of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)} implies that the problem has a unique optimal stopping time, which can be obtained as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t^{*}=\min \left\{t \in N \mid \frac{t}{N} \geq V_{t}^{*}(0)\right\}}
Figure 1 illustrates the variation in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{t}{N}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)} for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N=40} .
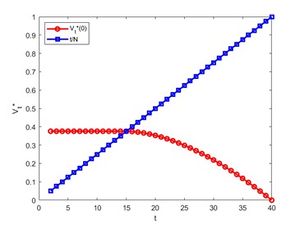
We know that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)=E\left\{V_{t+1}^{*}\left(x_{t+1}^{r}\right)\right\}=\frac{\tau}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(0)+\frac{1}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(1)} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(0)+\frac{1}{t+1} \max \left\{\frac{t+1}{N}, V_{t+1}^{*}(0)\right\}}
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t \geq t^{*}} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)=\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(0)+\frac{1}{t+1} \frac{t+1}{N}=\frac{t}{t+1} V_{t+1}^{*}(0)+\frac{1}{N}}
Using induction, it is easy to show that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t}^{*}(0)=\frac{t}{N} \sum_{k=t}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k}}
Hence, for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t^{*}} we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t^{*}=\min \left\{t \in N \mid \frac{t}{N} \geq \frac{t}{N} \sum_{k=t}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k}\right\}=\min \left\{t \in N \mid \sum_{k=t}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k} \leq 1\right\}}
It can be easily shown that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{t}-\frac{1}{N}\right)+\ln \left(\frac{N}{t}\right)<\sum_{k=t}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k}<\ln \left(\frac{N-1}{t-1}\right)}
Knowing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_{t-1}^{*}(0) \geq V_{t}^{*}(0)} and the definition of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t^{*}} , we can claim:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ln \left(\frac{N}{t}\right)<\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{t}-\frac{1}{N}\right)+\ln \left(\frac{N}{t}\right)<\sum_{k=t}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k} \leq 1<\sum_{k=t-1}^{N-1} \frac{1}{k}<\ln \left(\frac{N-1}{t-2}\right)}
Therefore, we can write:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ln \left(\frac{N}{t}\right)<1 \rightarrow t>\frac{N}{e}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ln \left(\frac{N-1}{t-2}\right)>1 \rightarrow t<\frac{N}{e}+2-\frac{1}{e}}
It can be concluded that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{N}{e}<t^{*}<\frac{N}{e}+2-\frac{1}{e}}
As Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t^{*}} is an integer, we can write:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{N}{e}<t^{*}<\frac{N}{e}+2-\frac{1}{e}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lceil{\frac{N}{e}}\rceil \leq t^{*} \leq \lfloor{\frac{N}{e}+2-\frac{1}{e}}\rfloor}
It is easy to show that as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N \rightarrow \infty, t^{*} \rightarrow\left[\frac{N}{e}\right]} , and the probability of picking the best secretary Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J^{*} \rightarrow \frac{1}{e}} .
Applications: Fields
Water resources and reservoir operation
Water needs to be stored in reservoirs for hydropower generation. The effect of storing water on downstream ecosystems has to be considered when constructing dams [12]. In fact, it is of paramount importance to let some water flow into the downstream to make sure the system is ecologically sustainable. The optimal flowrate released into the downstream, known as the minimum environmental flow, should be determined as it directly affects the hydropower generation and the associated benefit. Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP) has established itself as a powerful technique for analyzing hydropower systems and scheduling reservoir operation. The key state of such problems is the reservoir storage level. The objective is to maximize the associated revenue that can be obtained from hydropower generation. The SDP problem determines the optimal release rate in each stage. The problem is affected by the inherent uncertainty in the streamflows throughout the river basin [13].
Production planning
The problem of production planning involves determining the production and, if applicable, the loss of the demand in each stage to minimize the total production and storage cost during a time horizon. The production capacity limits, warehouse capacity limits, lot size, and demand act as the constraints of this problem. Uncertainty is inherently available on account of erroneous predictions of the demand, processing cost, and resource availability [14]. A similar application is the problem of recycling via manufacturing, namely remanufacturing. The degree of complexity and uncertainty in those problems is even greater than that in regular production planning problems [15]. Apart from the enumerated uncertainties above, the quality of the returned products is uncertain as the products were used by different people under different conditions. In addition, the returns may be from different companies and of different types adding more uncertainty to the problem.
Animal husbandry
SDP has also been applied to the problem of determining the replacement policy that is economically optimal in swine breeding herds [16]. The objective is to maximize the total profit that can be achieved given the number of existing sows in the herd and also the number of the replacement gilts over a planning horizon. As every other dynamic programming problem, the process starts from the last stage and proceeds backwards. The value that can be achieved from the available sows at the final stage is their slaughter value. The decision is to either keep or replace a sow. The problem is prone to uncertainty owing to involuntary reasons for culling sows such as disease or death and different reproduction characteristic between individual sows available in the herd.
Agriculture
SDP has been utilized to deal with the problem of weed control. Sells has found SDP more powerful than simulation-based approaches in determining the optimal weed control strategies [17]. The weed seedbanks of the available weeds can be regarded as the state vector. The decision to be made can be the type of crop to cultivate, time of planting, cultivations prior to planting, type of herbicide, rate of herbicide used, and time of spraying herbicide. The objective function to be minimized can be the total expected cost over a long planning horizon. Uncertainty needs to be considered in such problems due to uncertain performance of herbicides.
Energy systems
SDP has been applied to the storage management problem. Xi et al. developed an SDP model for determining the optimal use of a residential energy storage for different applications, namely meeting the energy demand of a building and providing regulation reserves to the grid, under uncertainty [18]. The objective is to maximize the total expected profit that can be obtained over a planning horizon by participating in both the energy and ancillary services markets. The decision variables are the amount of energy that needs to be charged and discharged during each time step. The optimal decision depends on the price in the energy and ancillary services markets, whether a power outage has happened or not, and the building energy demand. The prices in the two markets and the uncertain building energy demand expose the problem to uncertainty. As another example, SDP was deployed for managing a hybrid energy storage of an electric vehicle under the uncertainty arising from the driving cycle [19]. The state vector in this problem consisted of the velocity, power, and state of charge of the added double layer capacitors (making the storage hybrid). The control input was the battery current, and the objective was to minimize the total expected cost comprising a term associated with the loss of energy and a penalty term penalizing the deviation from the medium state of charge. The penalty term was important to be included in the formulation of the cost function as the prediction horizon of the SDP was short.
Conclusions
Stochastic Dynamic Programming is a technique that recursively solves stochastic optimization problems. Given a known state at the beginning of a discrete time period, Stochastic Dynamic Programming determines the optimal action that maximizes (minimizes) the expected total reward (cost) that can be achieved in that stage and the following ones. Starting from the boundary condition (typically the last stage), the optimal action in each stage is recursively determined for different possible states. The sequence of optimal actions is then selected based on the initial state and the consequent state transitions. Clearly specifying the state and the stage is of the utmost importance in all dynamic programming problems. Unlike in deterministic problems, the probability of transition from one state to another also affects the reward (cost) obtained (incurred) and, in turn, affects the optimal action. Stochastic Dynamic Programming has been applied to a variety of applications in different research fields ranging from energy systems to animal husbandry.
References
- ↑ Cho, K.B. (2017). ”Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP) and Sample Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SSDP) for Optimization of Korean Hydropower Plant”, Computers and Operations Research, 36(8): 2418–2428.
- ↑ Cardwell, Hal and Hugh Ellis (1993). "Stochastic Dynamic Programming Models for Water Quality Management", Water Resources Research, 29(4): 803-813.
- ↑ Cristobal, M. P., Escudero, L. F. and Monge, J. F. (2009). ”On stochastic dynamic programming for solving large-scale planning problems under uncertainty”, Computers and Operations Research, 36(8): 2418–2428.
- ↑ Huirne, R. B. M. et al. (1993). ”Stochastic dynamic programming to support sow replacement decisions”, European Journal of Operational Research, 67(2): 161–171.
- ↑ Xi, X., Sioshansi, R. and Marano, V. (2014). ”A stochastic dynamic programming model for co-optimization of distributed energy storage”, Energy Systems, 5(3): 475–505.
- ↑ Eum, Hyung-Il, Young-Oh Kim and Richard N. Palmer (2009). "Optimal Drought Management Using Sampling Stochastic Dynamic Programming with a Hedging Rule", Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management, 137(1): 113-122
- ↑ Johannesson, Lars, Mattias Asbogard and Bo Egardt (2007). "Assessing the Potential of Predictive Control for Hybrid Vehicle Powertrains Using Stochastic Dynamic Programming," IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 8(1): 71-83
- ↑ Westphal, Michael (2003). "The Use of Stochastic Dynamic Programming in Optimal Landscape Reconstruction for Metapopulations", Ecological Applications, 13(2): 543-555.
- ↑ Birge, J. R and Louveaux, F. (2011). ”Introduction to Stochastic Programming” (2nd ed.), Springer, p. 341-441.
- ↑ Bellman, R. (1972). ”Dynamic Programming” (6th ed.), Princeton University Press, p. 65-115.
- ↑ Powell, W. B. (2008). ”What You Should Know About Approximate Dynamic Programming”, Wiley InterScience.
- ↑ Cho, K.B. (2017). ”Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SDP) and Sample Stochastic Dynamic Programming (SSDP) for Optimization of Korean Hydropower Plant”, Computers and Operations Research, 36(8): 2418–2428.
- ↑ Kelman, J. et al. (1990). ”Sampling stochastic dynamic programming applied to reservoir operation”, Water Resources Research, 26(3): 447–454.
- ↑ Cristobal, M. P., Escudero, L. F. and Monge, J. F. (2009). ”On stochastic dynamic programming for solving large-scale planning problems under uncertainty”, Computers and Operations Research, 36(8): 2418–2428.
- ↑ Li, C. et al. (2009). ”A stochastic dynamic programming based model for uncertain production planning of re-manufacturing system”, International Journal of Production Research, 47(13): 3657–3668.
- ↑ Huirne, R. B. M. et al. (1993). ”Stochastic dynamic programming to support sow replacement decisions”, European Journal of Operational Research, 67(2): 161–171.
- ↑ Sells, J. E. (1995). ”Optimising weed management using stochastic dynamic programming to take account of uncertain herbicide performance”, Agricultural Systems, 48(3): 271-296.
- ↑ Xi, X., Sioshansi, R. and Marano, V. (2014). ”A stochastic dynamic programming model for co-optimization of distributed energy storage”, Energy Systems, 5(3): 475–505.
- ↑ Romaus, C., Gathmann, K. and Böcker, J. (2010). ”Optimal energy management for a hybrid energy storage system for electric vehicles based on stochastic dynamic programming”, 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, VPPC 2010.