Trust-region methods: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Author: Tung-Yen Wang (tw565) (CHEME 6800, Fall 2024) | |||
Stewards: Nathan Preuss, Wei-Han Chen, Tianqi Xiao, Guoqing Hu | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
Trust region method | Trust region methods are iterative optimization techniques designed to find local minima or maxima of objective functions, particularly in nonlinear problems (NLP), by iteratively refining approximations within dynamically adjusted trust regions<ref>Nocedal, J., & Wright, S. J. (2006). <em>Numerical optimization</em>. Springer.</ref>. Unlike line search methods, which determine the step size along a predefined direction, trust region methods concurrently optimize both the direction and the magnitude of the step within a specified neighborhood around the current iterate. | ||
= | |||
The origins of these methods date back to Levenberg, who introduced a modified version of the Gauss-Newton method for solving nonlinear least squares problems by adding a damping term to control the step size. This approach was later rediscovered and refined by Morrison and Marquardt, ultimately gaining prominence as the Levenberg-Morrison-Marquardt method <ref>Yuan, Y. (2015b). Recent advances in trust region algorithms. <em>Mathematical Programming</em>, 151(1), 249–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-015-0893-2</ref>. Subsequent advancements led to the development and standardization of trust region methods, further improving their robustness and application. | |||
The central core of trust region methods lies in the idea of constructing a simplified model — often a quadratic approximation — that represents the objective function near the current point. This model serves as a surrogate, guiding the search for the optimum within a bounded region around the current estimate. The size of the trust region is dynamically adjusted based on how well the model predicts the actual behavior of the objective function. If the model is predicting accurate behavior of the objective function, the size of the trust region is increased, allowing the algorithm to explore a larger area around the current solution; the trust region is reduced if otherwise <ref>Conn, A. R., Gould, N. I. M., & Toint, P. L. (2000). <em>Trust-region methods</em>. Siam.</ref>. | |||
=Algorithm Discussion= | |||
The mathematical framework involved in trust region methods starts with the construction of a local approximation of the objective function and defining a constrained region within which this model is trusted to be accurate. Consider the following local quadratic approximation of <math>f</math> around <math>x_k</math>: | |||
(1) <math>m_k(p) = f_k + \nabla f_k^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^T B_k p | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>p | |||
</math> represents the step or direction vector from the current point, <math>f_k=f(x_k) | |||
</math>, <math>\nabla f_k = \nabla f(x_k) | |||
</math>, and <math>B_k | |||
</math> is a symmetric matrix. | |||
The first two terms <math>m_k(p) | |||
</math> are designed to match the first two terms of the Taylor series expansion of <math>f(x_k+p) | |||
</math>. The expression can also be written as: | |||
<math>m_k(p) = f_k + \nabla f_k^T p + O(||p||^2) | |||
</math> | |||
where higher-order terms <math>O(||p||^2) | |||
</math> are approximated using <math>B_k | |||
</math>. It can also be noted that the difference between <math>m_k(p) | |||
</math> and <math>f(x_k+p) | |||
</math> is of order <math>O(||p||^2) | |||
</math>, suggesting that when p is small, the approximation error is minimal. | |||
For each iteration, seek a solution of the subproblem: | |||
(2) <math>m_k(p) = f_k + \nabla f_k^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^T B_k p | |||
</math> <math>s.t. ||p|| \leq \Delta_k | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>\Delta_k | |||
</math> represents the trust region radius and is greater than 0. | |||
Here, <math>p_k | |||
</math> represents the step taken at iteration <math>k | |||
</math>, hence the next point calculated can be denoted as <math>x_k+1=x_k+p | |||
</math>. For the moment, <math>|| \cdot || | |||
</math> is the Euclidean norm. | |||
To solve the subproblem, the trust region radius <math>k | |||
</math> must be determined at each iteration. | |||
(3) <math>p_k=\frac{f(x_k) - f(x_k+p_k)}{m_k(0) - m_k(p_k)} = \frac{actual\; reduction}{predicted\; reduction} | |||
</math> | |||
If <math>p_k | |||
</math> is negative, the objective value <math>f(x_k+p) | |||
</math> would be greater than the current value <math>f(x_k) | |||
</math>, leading to the rejection of the step. If <math>p_k | |||
</math> is positive but not close to 1, the trust region remains unchanged. If <math>p_k | |||
</math> is positive but close to 0, the trust region radius <math>\Delta_k | |||
</math> is reduced. On the other hand, if <math>p_k | |||
</math>is approximately equal to 1, the trust region radius <math>\Delta_k | |||
</math> is expanded for the next point iteration [1]. | |||
===Cauchy Point=== | |||
Identical to line search, there is no need to compute the subproblem (2) to achieve optimal minimum as the model improves itself with each iteration, meaning that as long as the step lies in the trust region and provides sufficient reduction, the algorithm can converge to the best solution. This sufficient reduction can be expressed as the Cauchy Point, that is: | |||
(4) <math>p_k^C =-\tau_k\frac{\Delta_k}{||\nabla f_k||} | |||
</math> | |||
where | |||
<math>\tau_k= \begin{cases} 1, & \text{if }\nabla f_k^TB_k\nabla f_k \leq 0\\ min(\frac{||\nabla f_k||^3}{\Delta _k\nabla f_k^TB_k\nabla f_k}, 1), & \text{if otherwise} \end{cases} | |||
</math> | |||
<math> | Computations often start with this as it is simple to calculate. To achieve better performance, however, it is necessary to integrate information about <math>B_k | ||
</math> to refine <math>p_k | |||
</math>. Consider the following: | |||
<math>p_B= -B_k^{-1} \nabla f_k | |||
</math> | |||
as the full Newton step where <math>||p_k||\leq \Delta_k | |||
</math>. | |||
===The Dogleg Method=== | |||
The full Newton step, however, is not feasible when the trust region constraint is active. To handle such cases, the Dogleg method is used to approximate the subproblem (2). This method finds a solution that considers two line segments. The first line is the steepest descent direction: | |||
<math>p^U =-\frac{g^Tg}{g^TB_g}g | |||
</math> | |||
<math> | where <math>g= \nabla f(x_k) | ||
</math>. | |||
The second line runs from <math>p^U | |||
</math> to <math>p^B | |||
</math> for <math>\tau\in [0,2] | |||
</math>: | |||
<math>p(\tau)= \begin{cases} \tau p^U & 0\leq \tau\leq 1\\ p^U+(\tau -1)(p^B-p^U) & 1\leq \tau\leq 2\end{cases} | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>p^B= -B^{-1}f(x_k) | |||
</math>. | |||
The | The method works well when <math>B_k | ||
</math> is positive definite. However, when <math>B_k | |||
</math> is not convex, <math>p_B | |||
</math> cannot guaranteed to be a meaningful solution since the method is not well-suited to handle negative <math>B_k | |||
</math>. | |||
===The Conjugated Gradient Steihaug’s Method=== | |||
In contrast to the methods above, Steihaug’s method is designed to better handle large-scale trust region subproblems. It mitigates the limitations of slower convergence and the need for a positive definite Hessian. In addition, it handles negative curvature by enabling early termination when such directions are detected or when the trust region boundary is reached. These features make the method more scalable and robust, suited for large-scale or poorly conditioned optimization problems <ref>Grippo, L., & Sciandrone, M. (2023). Introduction to Methods for Nonlinear Optimization. In <em>Unitext</em>. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26790-1</ref>. The method is described as follows: | |||
<math>\ | given <math>\varepsilon > 0 | ||
</math> | |||
<math> | set <math>p_0 = 0, r_0= g, d_0=-g,j=0 | ||
</math>; | |||
if <math>||r_0||< \varepsilon | |||
</math> | |||
:return <math>p_0 = p_j | |||
</math>; | |||
for all <math>j | |||
</math>, | |||
:if <math>d_j^TBd_j\leq0 | |||
</math> | |||
::determine <math>\tau | |||
</math> such that <math>p=p_j+\tau d_j | |||
</math> minimizes (2) and satisfies <math>||p|| = \Delta | |||
</math> | |||
::return <math>p | |||
</math>; | |||
:set <math>\alpha _j =\frac{r_j^Tr_j}{d_j^TBd_j} | |||
</math>; | |||
:set <math>p_{j+1} = \alpha _jd_j | |||
</math>; | |||
:if <math>||p_{j+1}|| \geq \Delta | |||
</math>; | |||
::determine the positive value of <math>\tau | |||
</math> such that <math>p=p_j+\tau d_j | |||
</math> and satisfies <math>||p|| = \Delta | |||
</math> | |||
::return <math>p | |||
</math>; | |||
:set <math>r_{j+1}=r_j+\alpha_jBd_j | |||
</math>; | |||
:if <math>||r_{j+1}|| \leq \varepsilon | |||
</math> | |||
::return <math>p=p_{j+1} | |||
</math>; | |||
:set <math>\beta_{j+1}=\frac{r_{j+1}^Tr_{j+1}}{r_{j+1}r_j} | |||
</math>; | |||
:set <math>d_{j+1}= -r_{j+1}+\beta_{j+1}d_j | |||
</math>; | |||
end (for) | |||
The initialization of <math>p_0 = 0 | |||
</math> is fundamental, as the Cauchy Point is obtained right after in <math>p_1 | |||
</math>; this condition guarantees global convergence. | |||
===Termination Criteria=== | |||
The convergence of a trust region algorithm (1) depends on the accuracy of the approximate solution to the subproblem (2). It is desirable that the subproblem is approximated rather than solved exactly, provided the approximation guarantees the algorithm’s convergence <ref>Dutta, S. (2016). <em>Optimization in Chemical Engineering</em>. Cambridge University Press.</ref>. Fletcher proposes that the algorithm terminates when either of the following are small <ref>Fletcher, R. (1987). <em>Practical Methods of Optimization</em> (2e), John Wiley and Sons.</ref>: | |||
# <math>f(x_k)-f(x_{k+1}) | |||
</math> | |||
# <math>x_k-x_{k+1} | |||
</math> | |||
# <math>\nabla f(x_k) | |||
</math> | |||
These criteria ensure that the algorithm terminates efficiently while maintaining convergence. | |||
In addition, termination can be considered when <math>\Delta_k | |||
</math> is small as it is possible for <math>\Delta_k | |||
</math> to converge to 0 when <math>k | |||
</math> approaches infinity. | |||
=Numerical example= | =Numerical example= | ||
===Example One=== | |||
'''This section introduces trust region methods and demonstrates their application using a simple function as a numerical example. Consider the following: | |||
<math>f(x)=(x-2)^2 | |||
</math> | |||
Our goal is to minimize this function, and clearly, the solution is <math>x=2 | |||
</math> where <math>f(2)=0 | |||
</math>. | </math>. | ||
The gradient is <math>f'(x)=2(x-2) | |||
</math> and the Hessian is <math>f''(x)=2 | |||
</math>. | |||
'''Iteration 1:''' | '''Iteration 1:''' | ||
To calculate, begin the initial point at <math>x_0=0 | |||
</math> and a trust region radius as <math>1.0 | |||
</math>. From this initial point, the following is obtained: | |||
Step 1: evaluate the current point: | |||
<math>f(x_0)=(0-2)^2=4 | |||
</math> | |||
Gradient: <math>f'(x_0)=2(0-2)=-4 | |||
</math> | |||
</math> | |||
</math>. | Hessian: <math>2 | ||
</math> | |||
Step 2: form the quadratic model | |||
<math>m_0(p) = f(x_0) + \nabla f_0^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^T H_0 = m_0(p) = 4 + (-4) p + \frac{1}{2} p^2(2)=4-4p+p^2 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 3: solve the subproblem | |||
<math>m_0'(p)=-4+2p=0 | |||
</math> <math>p=2 | |||
</math> | |||
However, <math>p=2 | |||
</math> is outside the trust region radius <math>1.0 | |||
</math>. Hence, <math>|p|\leq 1 | |||
</math> will be utilized to find the best step. | |||
<math>m_0(1)=4-4(1)+1^2=1 | |||
</math> | |||
<math>m_0(-1)=4-4(-1)+(-1)^2=9 | |||
</math> | |||
The lower value is <math>p=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 4: check function reduction | |||
Proposed new point: <math>x_1=x_0+p=0+1=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Actual function at new point: <math>f(1)=(1-2)^2=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 5: compute ratio | |||
Actual reduction: <math>f(x_0)-f(x_1)=4-1=3 | |||
</math> | |||
Prediction reduction: <math>f(x_0)-m_0(1)=4-1=3 | |||
</math> | |||
Hence <math>p=\frac{3}{3}=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 6: update trust region and accept/reject step | |||
Acceptant criteria for the ratio are typically as follows (may vary): | |||
If <math>p<0.25 | |||
</math>, reduce the trust region radius, if <math>p>0.75 | |||
</math>, expand the trust region radius. | |||
In the example, <math>p | |||
</math> is greater than <math>p>0.75 | |||
</math>, thus the trust region should be expanded and the step is accepted. Suppose the trust region radius is doubled (i.e. to <math>2.0 | |||
</math>). | |||
'''Iteration 2: ''' | |||
The point now is at <math>x_1=1 | |||
</math> and a radius as <math>2.0 | |||
</math>. From this point, the following is obtained: | |||
Step 1: evaluate the current point: | |||
<math>f(1)=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Gradient: <math>f'(1)=2(1-2)=-2 | |||
</math> | |||
Hessian: <math>2 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 2: form the quadratic model | |||
<math>m_1(p) = f(1) + \nabla f_0^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^TH_1= 1-2p+p^2 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 3: solve the subproblem | |||
<math>m_1'(p)= -2+2p =0 | |||
</math> <math>p=1 | |||
</math> | |||
<math>p\leq 2 | |||
</math>, then <math>p=1 | |||
</math> is valid | |||
Step 4: check function reduction | |||
Proposed new point: <math>x_2=x_1+1=2 | |||
</math> | |||
Actual function at new point: <math>f(2)=(2-2)^2=0 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 5: compute ratio | |||
Actual reduction: <math>f(1)-f(2)=1-0=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Prediction reduction: <math>f(1)-m_1(1)=1-0=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Hence <math>p=\frac{1}{1}=1 | |||
</math> | |||
Step 6: update trust region and accept/reject step | |||
In the example, since <math>p | |||
</math> is greater than <math>p>0.75 | |||
</math>, the proposed step is accepted. By taking this step, the problem reaches the exact minimum is reached at <math>x=2 | |||
</math>, and therefore terminates. | |||
===Example Two - Himmulblau’s Function=== | |||
</ | The following demonstrates a more complex example of trust region methods. Himmulblau’s function is a well-known mathematical function used extensively in optimization testing and research <ref>Himmelblau, D. M. (2018). <em>Applied nonlinear programming</em>. McGraw-Hill.</ref>. It is defined as two real variables and is characterized by having multiple global minima. The function is non-convex and multimodal, making it an excellent candidate for demonstrating the effectiveness of optimization algorithms. The following uses Steihaug’s method. | ||
The function is defined as the following: | |||
< | <math>f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2 | ||
</math> | |||
where <math>x | |||
</math> and <math>y | |||
</math> are real numbers. | |||
The four global minima of the function are at: | |||
</math>, | # <math>(3.0,2.0) | ||
</math> | |||
# <math>(-2.805, 3.131) | |||
</math> | |||
# <math>(-3.779,-3.283) | |||
</math> | |||
# <math>(3.584,-1.848) | |||
</math> | |||
[[File:Trust-Region-Radius.png|300px|right|thumb|The figure illustrates how the trust region radius adjusts throughout the optimization process, reflecting the optimizer’s confidence in the model’s predictions.]] | |||
. | Due to the complexities in the calculations involved in the trust region method algorithm, the '''minimize''' function with the '''<nowiki/>'trust-constr'''' method from the SciPy library in Python can be utilized to solve this problem. Consider the following implementation: | ||
'''minimize(method=’trust-constr’)''' | |||
'''Iteration 1:''' | |||
To calculate, begin the optimization with the initial guess as <math>(-4.0, 0) | |||
</math> and trust region radius as <math>1.0 | |||
</math>. The optimal solution achieved from this iteration is <math>(-3.382, -0.786) | |||
</math>, yield a function value of <math>95.453 | |||
</math>. The initial point gives a sufficient prediction, thus, increase the trust region radius to <math>7.0 | |||
</math>. | |||
[[File:Trust-Region-Heatmap.png|300px|right|thumb|The figure shows the trajectory of the optimizer from the initial guess to the found minimum over the contour plot of Hummuelblau’s function.]] | |||
'''Iteration 2:''' | |||
In this iteration, the updated point <math>(-4.0, 0) | |||
</math> and radius <math>7.0 | |||
</math> are used to find a new step. However, an insufficient prediction was obtained, leading to a decrease in the trust region radius to <math>0.7 | |||
</math>. The optimal solution obtained from the previous iteration is retained for the next step. | |||
'''Iteration 3:''' | |||
With the updated point <math>(-3.382, -0.786) | |||
</math> trust region radius <math>0.7 | |||
</math>, a new point at <math>(-3.072, -1.413) | |||
</math> was obtained. | |||
The following shows the remaining iterations: <br> | |||
[[File:Iterations.png|500px|Caption]] <br> | |||
The convergence achieved at iteration 11 with <math>x=-3.779,y= -3.283 </math> and <math>f(x) = 0</math>. | |||
= | =Applications= | ||
Trust region methods are applied in optimization problems across various domains due to their robustness, adaptability, and efficiency in handling complex constraints. Their ability to balance local and global optimization strategies makes them invaluable in solving high-dimensional, nonlinear, and constrained problems. These application areas include: | |||
= | ===Engineering=== | ||
Trust region methods are widely used in engineering, particularly in structural optimization, to improve the stability and efficiency of design processes. These methods address challenges in high-dimensional design problems by iteratively refining solutions with defined trust regions,making them effective for complex objectives such as optimization of material distribution, minimizing stress, or improving flow geometries. For instance, Yano et al. <ref>Yano, M., Huang, T., & Zahr, M. J. (2021). A globally convergent method to accelerate topology optimization using on-the-fly model reduction. <em>Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering</em>, 375, 113635–113635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113635</ref> introduce a globally convergent method to accelerate topology optimization with trust region frameworks. This approach significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining accuracy in optimal design solutions. | |||
===Finance=== | |||
Trust region methods are also increasingly applied in the financial sector as these methods ensure stable and reliable convergence even when dealing with complex, non-linear and volatile financial data. For example, in the study by Phua et al. <ref>Phua, P. K. H., Xiaotian Zhu, & Chung Haur Koh. (n.d.). Forecasting stock index increments using neural networks with trust region methods. <em>Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks</em>, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcnn.2003.1223354</ref>, trust region methods were employed during the optimization of neural network training. This approach significantly improved the forecasting accuracy of major stick indices like DAX and NASDAQ by effectively managing high-dimensional and noisy financial datasets. | |||
===Machine Learning=== | |||
Algorithms like ACKTR (Actor-Critic using Kronecker-Factored Trust Region) use trust regions to improve training stabilities and sample efficiencies in deep reinforcement learning. Specifically, ACKTR uses an approximation of the natural gradient to maintain a trust region during updates, preventing large and unstable parameter changes. This benefits facilitation of applications in robotics and autonomous systems <ref>Wu, Y., Elman Mansimov, Grosse, R. B., Liao, S., & Ba, J. (2017). Scalable trust-region method for deep reinforcement learning using Kronecker-factored approximation. <em>Neural Information Processing Systems</em>, 30, 5279–5288.</ref>. | |||
=Conclusion= | |||
Trust region methods provide a robust and efficient framework for solving optimization problems through the construction of a region around the current solution where an accurate simplified model approximates the objective function. This approach ensures convergence, even for nonlinear and complex problems encountered in fields such as engineering. The algorithm’s advantage lies in its adaptability, dynamically adjusting the trust region based on the accuracy of the model’s predictions, thereby ensuring global and, in some cases, superlinear convergence <ref>Zhang, J., Wu, L., & Zhang, X. (2007). A Trust Region Method for Optimization Problem with Singular Solutions. <em>Applied Mathematics and Optimization</em>, 56(3), 379–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-007-9009-6</ref>. Future research directions may involve improving the scalability of trust region methods for high-dimensional problems, integrating them with machine learning frameworks for better predictive modeling <ref>Lin, C.-J., Weng, R. C., & S. Sathiya Keerthi. (2008). Trust Region Newton Method for Logistic Regression. <em>Journal of Machine Learning Research</em>, 9(22), 627–650. https://doi.org/10.1145/1390681.1390703</ref>, and developing more efficient techniques to handle constraints and uncertainties in real-world applications. | |||
=References= | |||
Latest revision as of 02:25, 13 December 2024
Author: Tung-Yen Wang (tw565) (CHEME 6800, Fall 2024)
Stewards: Nathan Preuss, Wei-Han Chen, Tianqi Xiao, Guoqing Hu
Introduction
Trust region methods are iterative optimization techniques designed to find local minima or maxima of objective functions, particularly in nonlinear problems (NLP), by iteratively refining approximations within dynamically adjusted trust regions[1]. Unlike line search methods, which determine the step size along a predefined direction, trust region methods concurrently optimize both the direction and the magnitude of the step within a specified neighborhood around the current iterate.
The origins of these methods date back to Levenberg, who introduced a modified version of the Gauss-Newton method for solving nonlinear least squares problems by adding a damping term to control the step size. This approach was later rediscovered and refined by Morrison and Marquardt, ultimately gaining prominence as the Levenberg-Morrison-Marquardt method [2]. Subsequent advancements led to the development and standardization of trust region methods, further improving their robustness and application.
The central core of trust region methods lies in the idea of constructing a simplified model — often a quadratic approximation — that represents the objective function near the current point. This model serves as a surrogate, guiding the search for the optimum within a bounded region around the current estimate. The size of the trust region is dynamically adjusted based on how well the model predicts the actual behavior of the objective function. If the model is predicting accurate behavior of the objective function, the size of the trust region is increased, allowing the algorithm to explore a larger area around the current solution; the trust region is reduced if otherwise [3].
Algorithm Discussion
The mathematical framework involved in trust region methods starts with the construction of a local approximation of the objective function and defining a constrained region within which this model is trusted to be accurate. Consider the following local quadratic approximation of around :
(1)
where represents the step or direction vector from the current point, , , and is a symmetric matrix.
The first two terms are designed to match the first two terms of the Taylor series expansion of . The expression can also be written as:
where higher-order terms are approximated using Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_k } . It can also be noted that the difference between Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_k(p) } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_k+p) } is of order Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle O(||p||^2) } , suggesting that when p is small, the approximation error is minimal.
For each iteration, seek a solution of the subproblem:
(2) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_k(p) = f_k + \nabla f_k^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^T B_k p } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle s.t. ||p|| \leq \Delta_k }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_k } represents the trust region radius and is greater than 0.
Here, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k } represents the step taken at iteration Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k } , hence the next point calculated can be denoted as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_k+1=x_k+p } . For the moment, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle || \cdot || } is the Euclidean norm.
To solve the subproblem, the trust region radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k }
must be determined at each iteration.
(3) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k=\frac{f(x_k) - f(x_k+p_k)}{m_k(0) - m_k(p_k)} = \frac{actual\; reduction}{predicted\; reduction} }
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k } is negative, the objective value Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_k+p) } would be greater than the current value Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_k) } , leading to the rejection of the step. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k } is positive but not close to 1, the trust region remains unchanged. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k } is positive but close to 0, the trust region radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_k } is reduced. On the other hand, if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k } is approximately equal to 1, the trust region radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_k } is expanded for the next point iteration [1].
Cauchy Point
Identical to line search, there is no need to compute the subproblem (2) to achieve optimal minimum as the model improves itself with each iteration, meaning that as long as the step lies in the trust region and provides sufficient reduction, the algorithm can converge to the best solution. This sufficient reduction can be expressed as the Cauchy Point, that is:
(4) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k^C =-\tau_k\frac{\Delta_k}{||\nabla f_k||} }
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau_k= \begin{cases} 1, & \text{if }\nabla f_k^TB_k\nabla f_k \leq 0\\ min(\frac{||\nabla f_k||^3}{\Delta _k\nabla f_k^TB_k\nabla f_k}, 1), & \text{if otherwise} \end{cases} }
Computations often start with this as it is simple to calculate. To achieve better performance, however, it is necessary to integrate information about Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_k }
to refine Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_k }
. Consider the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_B= -B_k^{-1} \nabla f_k }
as the full Newton step where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||p_k||\leq \Delta_k } .
The Dogleg Method
The full Newton step, however, is not feasible when the trust region constraint is active. To handle such cases, the Dogleg method is used to approximate the subproblem (2). This method finds a solution that considers two line segments. The first line is the steepest descent direction:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p^U =-\frac{g^Tg}{g^TB_g}g }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g= \nabla f(x_k) } .
The second line runs from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p^U } to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p^B } for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau\in [0,2] } :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p(\tau)= \begin{cases} \tau p^U & 0\leq \tau\leq 1\\ p^U+(\tau -1)(p^B-p^U) & 1\leq \tau\leq 2\end{cases} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p^B= -B^{-1}f(x_k) } .
The method works well when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_k } is positive definite. However, when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_k } is not convex, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_B } cannot guaranteed to be a meaningful solution since the method is not well-suited to handle negative Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_k } .
The Conjugated Gradient Steihaug’s Method
In contrast to the methods above, Steihaug’s method is designed to better handle large-scale trust region subproblems. It mitigates the limitations of slower convergence and the need for a positive definite Hessian. In addition, it handles negative curvature by enabling early termination when such directions are detected or when the trust region boundary is reached. These features make the method more scalable and robust, suited for large-scale or poorly conditioned optimization problems [4]. The method is described as follows:
given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon > 0 }
set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_0 = 0, r_0= g, d_0=-g,j=0 } ;
if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||r_0||< \varepsilon }
- return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_0 = p_j } ;
for all Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j } ,
- if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_j^TBd_j\leq0 }
- determine Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau } such that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=p_j+\tau d_j } minimizes (2) and satisfies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||p|| = \Delta }
- return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p } ;
- set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha _j =\frac{r_j^Tr_j}{d_j^TBd_j} } ;
- set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_{j+1} = \alpha _jd_j } ;
- if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||p_{j+1}|| \geq \Delta } ;
- determine the positive value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau } such that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=p_j+\tau d_j } and satisfies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||p|| = \Delta }
- return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p } ;
- set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r_{j+1}=r_j+\alpha_jBd_j } ;
- if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ||r_{j+1}|| \leq \varepsilon }
- return Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=p_{j+1} } ;
- set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_{j+1}=\frac{r_{j+1}^Tr_{j+1}}{r_{j+1}r_j} } ;
- set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{j+1}= -r_{j+1}+\beta_{j+1}d_j } ;
end (for)
The initialization of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_0 = 0 } is fundamental, as the Cauchy Point is obtained right after in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p_1 } ; this condition guarantees global convergence.
Termination Criteria
The convergence of a trust region algorithm (1) depends on the accuracy of the approximate solution to the subproblem (2). It is desirable that the subproblem is approximated rather than solved exactly, provided the approximation guarantees the algorithm’s convergence [5]. Fletcher proposes that the algorithm terminates when either of the following are small [6]:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_k)-f(x_{k+1}) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_k-x_{k+1} }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla f(x_k) }
These criteria ensure that the algorithm terminates efficiently while maintaining convergence.
In addition, termination can be considered when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_k } is small as it is possible for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_k } to converge to 0 when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k } approaches infinity.
Numerical example
Example One
This section introduces trust region methods and demonstrates their application using a simple function as a numerical example. Consider the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)=(x-2)^2 }
Our goal is to minimize this function, and clearly, the solution is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=2 } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(2)=0 } .
The gradient is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f'(x)=2(x-2) } and the Hessian is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f''(x)=2 } .
Iteration 1:
To calculate, begin the initial point at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_0=0 } and a trust region radius as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1.0 } . From this initial point, the following is obtained:
Step 1: evaluate the current point:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_0)=(0-2)^2=4 }
Gradient: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f'(x_0)=2(0-2)=-4 }
Hessian: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2 }
Step 2: form the quadratic model
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_0(p) = f(x_0) + \nabla f_0^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^T H_0 = m_0(p) = 4 + (-4) p + \frac{1}{2} p^2(2)=4-4p+p^2 }
Step 3: solve the subproblem
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_0'(p)=-4+2p=0 } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=2 }
However, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=2 } is outside the trust region radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1.0 } . Hence, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |p|\leq 1 } will be utilized to find the best step.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_0(1)=4-4(1)+1^2=1 }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_0(-1)=4-4(-1)+(-1)^2=9 }
The lower value is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=1 }
Step 4: check function reduction
Proposed new point: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_1=x_0+p=0+1=1 }
Actual function at new point: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(1)=(1-2)^2=1 }
Step 5: compute ratio
Actual reduction:
Prediction reduction: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x_0)-m_0(1)=4-1=3 }
Hence Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=\frac{3}{3}=1 }
Step 6: update trust region and accept/reject step
Acceptant criteria for the ratio are typically as follows (may vary):
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p<0.25 } , reduce the trust region radius, if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p>0.75 } , expand the trust region radius.
In the example, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p } is greater than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p>0.75 } , thus the trust region should be expanded and the step is accepted. Suppose the trust region radius is doubled (i.e. to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2.0 } ).
Iteration 2:
The point now is at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_1=1 } and a radius as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2.0 } . From this point, the following is obtained:
Step 1: evaluate the current point:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(1)=1 }
Gradient: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f'(1)=2(1-2)=-2 }
Hessian: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2 }
Step 2: form the quadratic model
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_1(p) = f(1) + \nabla f_0^T p + \frac{1}{2} p^TH_1= 1-2p+p^2 }
Step 3: solve the subproblem
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_1'(p)= -2+2p =0 } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=1 }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p\leq 2 } , then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=1 } is valid
Step 4: check function reduction
Proposed new point: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_2=x_1+1=2 }
Actual function at new point: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(2)=(2-2)^2=0 }
Step 5: compute ratio
Actual reduction: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(1)-f(2)=1-0=1 }
Prediction reduction: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(1)-m_1(1)=1-0=1 }
Hence Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p=\frac{1}{1}=1 }
Step 6: update trust region and accept/reject step
In the example, since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p } is greater than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle p>0.75 } , the proposed step is accepted. By taking this step, the problem reaches the exact minimum is reached at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=2 } , and therefore terminates.
Example Two - Himmulblau’s Function
The following demonstrates a more complex example of trust region methods. Himmulblau’s function is a well-known mathematical function used extensively in optimization testing and research [7]. It is defined as two real variables and is characterized by having multiple global minima. The function is non-convex and multimodal, making it an excellent candidate for demonstrating the effectiveness of optimization algorithms. The following uses Steihaug’s method.
The function is defined as the following:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x,y)=(x^2+y-11)^2+(x+y^2-7)^2 }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y } are real numbers.
The four global minima of the function are at:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (3.0,2.0) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-2.805, 3.131) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-3.779,-3.283) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (3.584,-1.848) }

Due to the complexities in the calculations involved in the trust region method algorithm, the minimize function with the 'trust-constr' method from the SciPy library in Python can be utilized to solve this problem. Consider the following implementation:
minimize(method=’trust-constr’)
Iteration 1:
To calculate, begin the optimization with the initial guess as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-4.0, 0) } and trust region radius as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1.0 } . The optimal solution achieved from this iteration is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-3.382, -0.786) } , yield a function value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 95.453 } . The initial point gives a sufficient prediction, thus, increase the trust region radius to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 7.0 } .

Iteration 2:
In this iteration, the updated point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-4.0, 0) } and radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 7.0 } are used to find a new step. However, an insufficient prediction was obtained, leading to a decrease in the trust region radius to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0.7 } . The optimal solution obtained from the previous iteration is retained for the next step.
Iteration 3:
With the updated point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-3.382, -0.786) } trust region radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0.7 } , a new point at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-3.072, -1.413) } was obtained.
The following shows the remaining iterations:
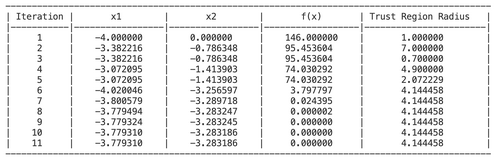
The convergence achieved at iteration 11 with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=-3.779,y= -3.283 }
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x) = 0}
.
Applications
Trust region methods are applied in optimization problems across various domains due to their robustness, adaptability, and efficiency in handling complex constraints. Their ability to balance local and global optimization strategies makes them invaluable in solving high-dimensional, nonlinear, and constrained problems. These application areas include:
Engineering
Trust region methods are widely used in engineering, particularly in structural optimization, to improve the stability and efficiency of design processes. These methods address challenges in high-dimensional design problems by iteratively refining solutions with defined trust regions,making them effective for complex objectives such as optimization of material distribution, minimizing stress, or improving flow geometries. For instance, Yano et al. [8] introduce a globally convergent method to accelerate topology optimization with trust region frameworks. This approach significantly reduces computational costs while maintaining accuracy in optimal design solutions.
Finance
Trust region methods are also increasingly applied in the financial sector as these methods ensure stable and reliable convergence even when dealing with complex, non-linear and volatile financial data. For example, in the study by Phua et al. [9], trust region methods were employed during the optimization of neural network training. This approach significantly improved the forecasting accuracy of major stick indices like DAX and NASDAQ by effectively managing high-dimensional and noisy financial datasets.
Machine Learning
Algorithms like ACKTR (Actor-Critic using Kronecker-Factored Trust Region) use trust regions to improve training stabilities and sample efficiencies in deep reinforcement learning. Specifically, ACKTR uses an approximation of the natural gradient to maintain a trust region during updates, preventing large and unstable parameter changes. This benefits facilitation of applications in robotics and autonomous systems [10].
Conclusion
Trust region methods provide a robust and efficient framework for solving optimization problems through the construction of a region around the current solution where an accurate simplified model approximates the objective function. This approach ensures convergence, even for nonlinear and complex problems encountered in fields such as engineering. The algorithm’s advantage lies in its adaptability, dynamically adjusting the trust region based on the accuracy of the model’s predictions, thereby ensuring global and, in some cases, superlinear convergence [11]. Future research directions may involve improving the scalability of trust region methods for high-dimensional problems, integrating them with machine learning frameworks for better predictive modeling [12], and developing more efficient techniques to handle constraints and uncertainties in real-world applications.
References
- ↑ Nocedal, J., & Wright, S. J. (2006). Numerical optimization. Springer.
- ↑ Yuan, Y. (2015b). Recent advances in trust region algorithms. Mathematical Programming, 151(1), 249–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10107-015-0893-2
- ↑ Conn, A. R., Gould, N. I. M., & Toint, P. L. (2000). Trust-region methods. Siam.
- ↑ Grippo, L., & Sciandrone, M. (2023). Introduction to Methods for Nonlinear Optimization. In Unitext. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-26790-1
- ↑ Dutta, S. (2016). Optimization in Chemical Engineering. Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Fletcher, R. (1987). Practical Methods of Optimization (2e), John Wiley and Sons.
- ↑ Himmelblau, D. M. (2018). Applied nonlinear programming. McGraw-Hill.
- ↑ Yano, M., Huang, T., & Zahr, M. J. (2021). A globally convergent method to accelerate topology optimization using on-the-fly model reduction. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 375, 113635–113635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2020.113635
- ↑ Phua, P. K. H., Xiaotian Zhu, & Chung Haur Koh. (n.d.). Forecasting stock index increments using neural networks with trust region methods. Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcnn.2003.1223354
- ↑ Wu, Y., Elman Mansimov, Grosse, R. B., Liao, S., & Ba, J. (2017). Scalable trust-region method for deep reinforcement learning using Kronecker-factored approximation. Neural Information Processing Systems, 30, 5279–5288.
- ↑ Zhang, J., Wu, L., & Zhang, X. (2007). A Trust Region Method for Optimization Problem with Singular Solutions. Applied Mathematics and Optimization, 56(3), 379–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00245-007-9009-6
- ↑ Lin, C.-J., Weng, R. C., & S. Sathiya Keerthi. (2008). Trust Region Newton Method for Logistic Regression. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 9(22), 627–650. https://doi.org/10.1145/1390681.1390703











