Trust-region methods
Autor: Chun-Yu Chou (cc2398), Ting-Guang Yeh (ty262), Yun-Chung Pan (yp392), Chen-Hua Wang (cw893), Fall 2021
Introduction
Problem formulation
Numerical example
Here we will use the trust-region method to solve a classic optimization problem, the Rosenbrock function. The Rosenbrock function is a non-convex function, introduced by Howard H. Rosenbrock in 1960, which is often used as a performance test problem for optimization algorithms. This problem is solved using MATLAB's fminunc as the solver, with 'trust-region' as the solving algorithm which uses the preconditioned conjugate method.
The function is defined by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \min f(x,y)=100(y-x^2)^2+(1-x)^2}
The starting point chosen is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0 } .
Iteration Process
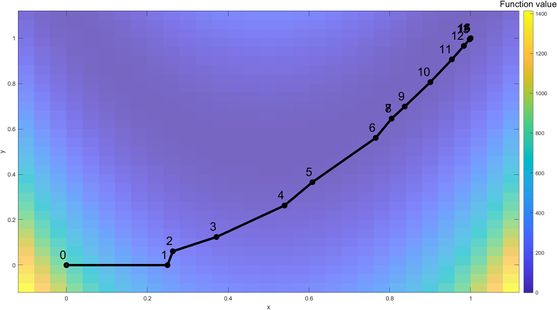
Iteration 1: The algorithm starts from the initial point of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0 } . The Rosenbrock function is visualized with a color coded map. For the first iteration, a full step was taken and the optimal solution (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.25} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0 } ) within the trust-region is denoted as a red dot.
Iteration 2: Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.25 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0 } . The new iteration gives a good prediction, which increases the trust-region's size. The new optimal solution within the trust-region is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.263177536 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.061095029 } .
Iteration 3: Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.263177536 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.061095029 } . The new iteration gives a poor prediction, which decreases the trust-region's size to improve the model's validity. The new optimal solution within the trust-region is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.371151679 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.124075855 } .
...
Iteration 7: Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.765122406 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.560476539 } . The new iteration gives a poor prediction, which decreases the trust-region's size to improve the model's validity. The new optimal solution within the trust-region is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.804352654 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.645444179 } .
Iteration 8: Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0.804352654 }
, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=0.645444179 }
.The new iteration gives a poor prediction, therefore current best solution is unchanged and the radius for the trust-region is decreased.
...
At the 16th iteration, the global optimal solution is found, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=1 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y=1 } .
| Iterations | f(x) | x | y | Norm of step | First-order optimality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.953125 | 0.263178 | 0.061095 | 0.25 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 0.549578 | 0.371152 | 0.124076 | 0.0625 | 1.63 |
| 4 | 0.414158 | 0.539493 | 0.262714 | 0.125 | 2.74 |
| 5 | 0.292376 | 0.608558 | 0.365573 | 0.218082 | 5.67 |
| 6 | 0.155502 | 0.765122 | 0.560477 | 0.123894 | 0.954 |
| 7 | 0.117347 | 0.804353 | 0.645444 | 0.25 | 7.16 |
| 8 | 0.0385147 | 0.804353 | 0.645444 | 0.093587 | 0.308 |
| 9 | 0.0385147 | 0.836966 | 0.69876 | 0.284677 | 0.308 |
| 10 | 0.0268871 | 0.90045 | 0.806439 | 0.0625 | 0.351 |
| 11 | 0.0118213 | 0.953562 | 0.90646 | 0.125 | 1.38 |
| 12 | 0.0029522 | 0.983251 | 0.9659 | 0.113247 | 0.983 |
| 13 | 0.000358233 | 0.99749 | 0.994783 | 0.066442 | 0.313 |
| 14 | 1.04121e-05 | 0.999902 | 0.999799 | 0.032202 | 0.0759 |
| 15 | 1.2959e-08 | 1 | 1 | 0.005565 | 0.00213 |
| 16 | 2.21873e-14 | 1 | 1 | 0.000224 | 3.59E-06 |