AdaGrad: Difference between revisions
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
AdaGrad is a family of sub-gradient algorithms for stochastic optimization. The algorithms belonging to that family are similar to second-order stochastic gradient descend with an approximation for the Hessian of the optimized function. AdaGrad's name comes from '''Ada'''ptative '''Grad'''ient. Intuitively, it adapts the learning rate for each feature depending on the estimated geometry of the problem; particularly, it tends to assign higher learning rates to infrequent features, which ensures that the parameter updates rely less on frequency and more on relevance. | AdaGrad is a family of sub-gradient algorithms for stochastic optimization. The algorithms belonging to that family are similar to second-order stochastic gradient descend with an approximation for the Hessian of the optimized function. AdaGrad's name comes from '''Ada'''ptative '''Grad'''ient. Intuitively, it adapts the learning rate for each feature depending on the estimated geometry of the problem; particularly, it tends to assign higher learning rates to infrequent features, which ensures that the parameter updates rely less on frequency and more on relevance. | ||
AdaGrad was introduced by Duchi et al.<ref name=":0">Duchi, J., Hazan, E., & Singer, Y. (2011). Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. ''Journal of machine learning research'', ''12''(7).</ref> in a highly cited paper published in the Journal of machine learning research in 2011. It is arguably one of the most popular algorithms for machine learning (particularly for training deep neural networks) and it influenced the development of the [[Adam|Adam algorithm]]<ref>Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. ''arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980''.</ref>. | AdaGrad was introduced by Duchi et al.<ref name=":0">Duchi, J., Hazan, E., & Singer, Y. (2011). Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. ''Journal of machine learning research'', ''12''(7).</ref> in a highly cited paper published in the Journal of machine learning research in 2011. It is arguably one of the most popular algorithms for machine learning (particularly for training deep neural networks) and it influenced the development of the [[Adam|Adam algorithm]]<ref name=":1">Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. ''arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980''.</ref>. | ||
== Theory == | == Theory == | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
<math display="block">G_1 = \sum_{\tau=1}^1 g_1g_1^{\top} = \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 & -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 387.30 & 151.14\\ 151.14 & 58.98\end{bmatrix} </math>So the first parameter's update is calculated as follows: | <math display="block">G_1 = \sum_{\tau=1}^1 g_1g_1^{\top} = \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 & -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 387.30 & 151.14\\ 151.14 & 58.98\end{bmatrix} </math>So the first parameter's update is calculated as follows: | ||
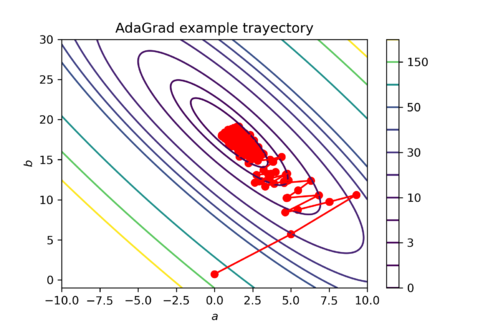
<math display="block">\begin{bmatrix} a_2 \\ b_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} 5 \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{387.30}} \\ 5\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{ 58.98}} \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 5 \\ 5\end{bmatrix}</math>This process is repetated until convergence or for a fixed number of iterations <math>T</math>. An example AdaGrad update trayectory for this example is presented in Figure 1. Note that in | <math display="block">\begin{bmatrix} a_2 \\ b_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} 5 \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{387.30}} \\ 5\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{ 58.98}} \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 5 \\ 5\end{bmatrix}</math>This process is repetated until convergence or for a fixed number of iterations <math>T</math>. An example AdaGrad update trayectory for this example is presented in Figure 1. Note that in Figure 1, the algorithm converges to a region close to <math>(a,b) = (0,20)</math>, which are the set of parameters that originated the obsevations in this example. | ||
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
The AdaGrad algorithm | The AdaGrad family of algorithms is typically used in machine learning applications. Mainly, it is a good choice for deep learning models with sparse input features. However, it can be applied to any optimization problem with a differentiable cost function. Given its popularity and proven performance, different versions of AdaGrad are implemented in the leading deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Nevertheless, in practice, AdaGrad tends to be substituted by the use of the Adam algorithm; since, for a given choice of hyperparameters, Adam is equivalent to AdaGrad <ref name=":1" />. | ||
== Summary and Discussion == | == Summary and Discussion == | ||
Revision as of 16:13, 28 November 2021
Author: Daniel Villarraga (SYSEN 6800 Fall 2021)
Introduction
AdaGrad is a family of sub-gradient algorithms for stochastic optimization. The algorithms belonging to that family are similar to second-order stochastic gradient descend with an approximation for the Hessian of the optimized function. AdaGrad's name comes from Adaptative Gradient. Intuitively, it adapts the learning rate for each feature depending on the estimated geometry of the problem; particularly, it tends to assign higher learning rates to infrequent features, which ensures that the parameter updates rely less on frequency and more on relevance.
AdaGrad was introduced by Duchi et al.[1] in a highly cited paper published in the Journal of machine learning research in 2011. It is arguably one of the most popular algorithms for machine learning (particularly for training deep neural networks) and it influenced the development of the Adam algorithm[2].
Theory
The objective of AdaGrad is to minimize the expected value of a stochastic objective function, with respect to a set of parameters, given a sequence of realizations of the function. As with other sub-gradient-based methods, it achieves so by updating the parameters in the opposite direction of the sub-gradients. While standard sub-gradient methods use update rules with step-sizes that ignore the information from the past observations, AdaGrad adapts the learning rate for each parameter individually using the sequence of gradient estimates.
Definitions
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(x)} : Stochastic objective function with parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_t(x)} : Realization of stochastic objective at time step Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} . For simplicity Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_t } .
: The gradient of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_t(x)} with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} , formally . For simplicity, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_t } .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t} : Parameters at time step Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} : The outer product of all previous subgradients, given by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\textstyle \sum_{\tau=1}^t g_{\tau}g_{\tau}^{\top} }
Standard Sub-gradient Update
Standard sub-gradient algorithms update parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} according to the following rule:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1} = x_t - \eta g_t} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} denotes the step-size often refered as learning rate or step-size. Expanding each term on the previous equation, the vector of parameters is updated as follows:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} x_{t+1}^{(2)} \\ x_{t+1}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ x_{t+1}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{t}^{(2)} \\ x_{t}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ x_{t}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} - \eta \begin{bmatrix} g_{t}^{(2)} \\ g_{t}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ g_{t}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} }
AdaGrad Update
The general AdaGrad update rule is given by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1} = x_t - \eta G_t^{-1/2} g_t} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t^{-1/2}} is the inverse of the square root of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} . A simplified version of the update rule takes the diagonal elements of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} instead of the whole matrix:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1} = x_t - \eta \text{diag}(G_t)^{-1/2} g_t} which can be computed in linear time. In practice, a small quantity Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} is added to each diagonal element in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} to avoid singularity problems, the resulting update rule is given by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_{t+1} = x_t - \eta \text{diag}(\epsilon I + G_t)^{-1/2} g_t} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I } denotes the identity matrix. An expanded form of the previous update is presented below,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} x_{t+1}^{(2)} \\ x_{t+1}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ x_{t+1}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} x_{t}^{(2)} \\ x_{t}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ x_{t}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} \eta \frac{1}{\sqrt{\epsilon + G_t^{(1,1)}}} \\ \eta \frac{1}{\sqrt{\epsilon + G_t^{(2,2)}}} \\ \vdots \\ \eta \frac{1}{\sqrt{\epsilon + G_t^{(m,m)}}} \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} g_{t}^{(2)} \\ g_{t}^{(2)} \\ \vdots \\ g_{t}^{(m)} \end{bmatrix} } where the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \odot} denotes the Hadamard product between matrices of the same dimension, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t^{(j,j)}} is the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j} element in the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} diagonal. From the last expression, it is clear that the update rule for AdaGrad adapts the step-size for each parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j} accoding to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\textstyle \eta (\epsilon + G_t^{(j,j)})^{-1/2}} , while standard sub-gradient methods have fixed step-size Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} for every parameter.
Adaptative Learning Rate Effect
An estimate for the uncentered second moment of the objective function's gradient is given by the following expression:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v = \frac{1}{t} \sum_{\tau=1}^t g_tg_t^{\top}}
which is similar to the definition of matrix Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} , used in AdaGrad's update rule. Noting that, AdaGrad adapts the learning rate for each parameter proportionally to the inverse of the gradient's variance for every parameter. This leads to the main advantages of AdaGrad:
- Parameters associated with low frequency features tend to have larger learning rates than parameters associated with high frequency features.
- Step-sizes in directions with high gradient variance are lower than the step-sizes in directions with low gradient variance. Geometrically, the step-sizes tend to decrease proportionally to the curvature of the stochastic objective function.
which favor the convergence rate of the algorithm.
Algorithm
The general version of the AdaGrad algorithm is presented in the pseudocode below. The update step within the for loop can be modified with the version that uses the diagonal of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t} .

Regret Bound
The regret is defined as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R(t) = \sum_{t= 1}^T f_{t}(x_t) - \sum_{t=1}^t f_{t}(x^*)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x^*} is the set of optimal parameters. AdaGrad has a regret bound of order Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle O(\sqrt{T})} , which leads to the convergence rate of order Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle O(1/\sqrt{T})} , and the convergence guarantee (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\textstyle \lim_{T \to \infty} R(T)/T = 0} ). The detailed proof and assumptions for this bound can be found in the original journal paper[1].
Numerical Example
To illustrate how the parameter updates work in AdaGrad take the following numerical example The dataset consists of random generated obsevations Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x,y } that follow the linear relationship:Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y = 20 \cdot x + \epsilon } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon} is random noise. The first 5 obsevations are shown in the table below.
| Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x } | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle y } |
|---|---|
| 0.39 | 9.83 |
| 0.10 | 2.27 |
| 0.30 | 5.10 |
| 0.35 | 6.32 |
| 0.85 | 15.50 |
The cost function is defined as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\textstyle f(a,b) = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^n ([a+b\cdot x_i]-y_i)^2} . And an observation of the cost function at time step Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t} is given by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_t(a,b) = ([a+b\cdot x_t]-y_t)^2} , where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_t, y_t} are sampled from the obsevations. Finally, the subgradient is determined by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_t = \begin{bmatrix} 2([a_t +b_t\cdot x_t]-y_t) \\ 2x_t ([a_t +b_t\cdot x_t]-y_t) \end{bmatrix}}
Take a learning rate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta = 5} , initial parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_1, b_1 = 0} , and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x_1= 0.39, y_1= 9.84} . For the first iteration of AdaGrad the subgradient is equal to:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g_1 = \begin{bmatrix} 2([0 +0\cdot 0.39]-9.84) \\ 2\cdot 0.39([0 +0\cdot 0.39]-9.84) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} }
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_t } is:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_1 = \sum_{\tau=1}^1 g_1g_1^{\top} = \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 & -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 387.30 & 151.14\\ 151.14 & 58.98\end{bmatrix} } So the first parameter's update is calculated as follows:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} a_2 \\ b_2 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} - \begin{bmatrix} 5 \cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{387.30}} \\ 5\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{ 58.98}} \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} -19.68 \\ -7.68 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 5 \\ 5\end{bmatrix}} This process is repetated until convergence or for a fixed number of iterations Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T} . An example AdaGrad update trayectory for this example is presented in Figure 1. Note that in Figure 1, the algorithm converges to a region close to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (a,b) = (0,20)} , which are the set of parameters that originated the obsevations in this example.
Applications
The AdaGrad family of algorithms is typically used in machine learning applications. Mainly, it is a good choice for deep learning models with sparse input features. However, it can be applied to any optimization problem with a differentiable cost function. Given its popularity and proven performance, different versions of AdaGrad are implemented in the leading deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Nevertheless, in practice, AdaGrad tends to be substituted by the use of the Adam algorithm; since, for a given choice of hyperparameters, Adam is equivalent to AdaGrad [2].

